

| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.K.A.1.1 (Archived) | Represent quantities with numbers up to 20, verbally, in writing, and with manipulatives. Remarks: Example: Have 20 plastic cups with numbers 1 through 20 on them. Have each student fill one cup with number of beans written on the cup. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.K.A.1.2 (Archived) | Solve problems including those involving sets by counting, by using cardinal and ordinal numbers, by comparing, by ordering, and by creating sets up to 20. Remarks: Students will compare sets by ordering numbers, by using concrete objects and by using appropriate language such as none, more than, fewer than, same number of, and one more than. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.K.A.1.3 (Archived) | Solve word problems involving simple joining and separating situations. Remarks: Students will use pictures and manipulatives to solve addition and subtraction problems. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.K.G.2.1 (Archived) | Describe, sort and re-sort objects using a variety of attributes such as shape, size, and position. Remarks: Students will use manipulatives. Position descriptions will include relative positions of objects in space such as beside, inside, outside, next to, above, and below. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.K.G.2.2 (Archived) | Identify, name, describe and sort basic two-dimensional shapes such as squares, triangles, circles, rectangles, hexagons, and trapezoids. Remarks: Descriptions of attributes of 2-Dimensional shapes include the number of sides and the number of vertices. Students will reproduce the shapes by drawing pictures. Teachers should restrict hexagons and trapezoids to regular hexagons and isosceles trapezoids. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.K.G.2.3 (Archived) | Identify, name, describe, and sort three-dimensional shapes such as spheres, cubes and cylinders. Remarks: Students will use manipulatives and real-world objects. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.K.G.2.4 (Archived) | Interpret the physical world with geometric shapes, and describe it with corresponding vocabulary.
Remarks: Students will use everyday examples to represent geometric shapes such as the edge of a clock to represent a circle and the edge of a ceiling tile to represent a rectangle. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.K.G.2.5 (Archived) | Use basic shapes, spatial reasoning, and manipulatives to model objects in the environment and to construct more complex shapes. Remarks: Students will create new objects from a set of given shapes. Students will reproduce a model by selecting the shapes represented in the model. For example, students may choose to create a representation of a house using a square and a triangle.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.K.G.3.1 (Archived) | Compare and order objects indirectly or directly using measurable attributes such as length, height, and weight. Remarks: Direct means that one object is compared to another. Example: The length of two crayons is compared to by placing them next to each other and stating which one is longer or shorter. Indirect means that a measurement is provided to allow the comparison. Example: One student's height is marked on the wall. Another student's height is marked on the wall. The two marks are compared to determine their relative height. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.K.A.4.1 (Archived) | Identify and duplicate simple number and non-numeric repeating and growing patterns. Remarks: Students will complete patterns according to shape, size, and color. Consider up to two attributes at a time. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.K.G.5.1 (Archived) | Demonstrate an understanding of the concept of time using identifiers such as morning, afternoon, day, week, month, year, before/after, shorter/longer. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.1.A.1.1 (Archived) | Model addition and subtraction situations using the concepts of "part-whole," "adding to," "taking away from," "comparing," and missing addend." Remarks: Teachers should ensure that students focus on conceptual understanding by using manipulatives, words, or pictures, and limiting the use of formal algorithms. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.1.A.1.2 (Archived) | Identify, describe, and apply addition and subtraction as inverse operations. Remarks: Example: 4 + 2 = 6 and 6 - 2 = 4. Example: List three other facts using addition or subtraction that are related to 3 + 5 = 8. Example: I have 8 marbles. Some are red. Some are blue. How many of each could I have? How many red marbles? How many blue marbles? Find as many combinations as you can. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.1.A.1.3 (Archived) | Create and use increasingly sophisticated strategies, and use properties such as Commutative, Associative and Additive Identity, to add whole numbers. Remarks: Example: 2 + 3 = 5 and 3 + 2 = 5 (Commutative Property) Example: 2 + (3 + 1) = 6 and (2 + 3 ) + 1 = 6 (Associative Property) Example: 7 + 8 = 7 + 7 + 1 (doubles + 1) Example: 9 + 4 = 10 + 3 (Using ten as a friendly number to add and subtract) Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.1.A.1.4 (Archived) | Use counting strategies, number patterns, and models as a means for solving basic addition and subtraction fact problems. Remarks: Decomposing considered key for understanding the addition and subtraction relationship. Teachers should include one-step word problems. Strategies include: Doubles, Doubles + 1, Doubles - 1, Grouping 10s, Counting on, and Counting back Example: 6 + 7 = 13, 6 + 6 + 1 = 13Example: 13 - 7 = 6 and (13 - 3) - 4 = 6 (using the knowledge that 3 + 4 = 7) Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.1.A.2.1 (Archived) | Compare and order whole numbers at least to 100. Remarks: Example: Is 86 larger than 68? Example: State whether 29 is larger than 38 or smaller than 38. Example: Name a number that comes between 70 and 75.Example: What number comes after 29?
|
| MA.1.A.2.2 (Archived) | Represent two digit numbers in terms of tens and ones. Remarks: Example: How many tens and how many ones are in fifty-six? Explain your answer. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.1.A.2.3 (Archived) | Order counting numbers, compare their relative magnitudes, and represent numbers on a number line. Remarks: Vocabulary should include use of the words: greater, greatest, smaller, and smallest. Show position of given whole numbers on the number line. Given a starting number and ending number on the number line, students decide whether to go left or right to get from the starting number to the ending number.Example: Arrange the numbers 5, 2, 9 in order from greatest to least. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.1.G.3.1 (Archived) | Use appropriate vocabulary to compare shapes according to attributes and properties such as number and lengths of sides and number of vertices.
Remarks: Activities should include classification of shapes.
|
| MA.1.G.3.2 (Archived) | Compose and decompose plane and solid figures, including making predictions about them, to build an understanding of part-whole relationships and properties of shapes.
Remarks: Example of composing: The student puts two congruent isosceles triangles together to make a rhombus.
Students can decorate necklaces by composing triangles (or other shapes) and find number of triangles or rhombuses needed for different necklaces with different lengths.
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.1.A.4.1 (Archived) | Extend repeating and growing patterns, fill in missing terms, and justify reasoning. Remarks: The student gains an understanding of skip counting. Example 1: What number comes next in this pattern {3, 6, 9, 12, 15, __}? Why? Example 2: What shape is missing in this pattern? Explain your answer.  Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.1.G.5.1 (Archived) | Measure by using iterations of a unit, and count the unit measures by grouping units.
Remarks: Measuring by using iterations involves multiple copies of a unit placed end-to-end and then counting the unit measures by grouping units. Use manipulatives such as cubes, rods, or other objects in the counting process. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.1.G.5.2 (Archived) | Compare and order objects according to descriptors of length, weight, and capacity.
Remarks: Descriptors of length would include words such as short, shorter, shortest, long, longer, longest, tall, taller, tallest, and high, higher, highest. Similar descriptors are used for weight and capacity. Activities should include the use of simple approximations to measure lengths and weights Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.1.A.6.1 (Archived) | Use mathematical reasoning and beginning understanding of tens and ones, including the use of invented strategies, to solve two-digit addition and subtraction problems. Remarks: Invented and standard algorithms should be explored to help students reason about joining, separating and comparing numbers, and about the relationship between tens and ones. Example: Adding 27 and 15, a student might reason that 27 is 20 + 7 and that 15 is 10 + 5. In determining the result, they combine 20 + 10=30 and 7 + 5 =12. The final answer involves the simpler addition problem of 30 + 12 is 42. Activities should include contexts such as money. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.1.A.6.2 (Archived) | Solve routine and non-routine problems by acting them out, using manipulatives, and drawing diagrams. Remarks: Students should be able to explain and justify their reasoning. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.2.A.1.1 (Archived) | Identify relationships between the digits and their place values through the thousands, including counting by tens and hundreds. Remarks: Example: Represent 2347 by using 3-dimensional base-10 blocks. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.A.1.2 (Archived) | Identify and name numbers through thousands in terms of place value, and apply this knowledge to expanded notation.
Remarks: Name and write in numeral whole numbers through 9,999. Identify the place value of the digits and order the numbers. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.2.A.1.3 (Archived) | Compare and order multi-digit numbers through the thousands. Remarks: Students will use less than, equal to, and greater than symbols (<, =, >). Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.2.A.2.1 (Archived) | Recall basic addition and related subtraction facts. Remarks: Basic facts include addends from zero through nine. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.2.A.2.2 (Archived) | Add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers through three digits with fluency by using a variety of strategies, including invented and standard algorithms and explanations of those procedures. Remarks: Activities include mental computation. Example: For 141 - 99, the standard algorithm uses regrouping. An invented approach may be to subtract 100 and add 1 (141-100+1). Another invented approach is to add one to both the minuend and subtrahend so that you have 142 - 100, which can be done mentally. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.A.2.3 (Archived) | Estimate solutions to multi-digit addition and subtraction problems through three digits. Remarks: Example: Your friend says that 247 + 65 = 897. Without solving, explain why you think the answer is wrong. Activities include mental computation. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.A.2.4 (Archived) | Solve addition and subtraction problems that involve measurement and geometry. Remarks: For example, students can add two units of the same measure (34 cm + 20 cm) Example: What is the total number of sides in two triangles?
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.2.G.3.1 (Archived) | Estimate and use standard units, including inches and centimeters, to partition and measure lengths of objects. Remarks: Example: Measure and compare common objects using metric and customary units of length, such as centimeters and inches. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.G.3.2 (Archived) | Describe the inverse relationship between the size of a unit and number of units needed to measure a given object. Remarks: Example: Suppose the perimeter of a room is lined with one-foot rulers. Now, suppose we want to line it with yardsticks instead of rulers. Will we need more or fewer yardsticks than rulers to do the job? Explain your answer. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.G.3.3 (Archived) | Apply the Transitive Property when comparing lengths of objects. Remarks: The Transitive Property states If object A is longer than object B, and object B is longer than object C, then object A is longer than object C.   Label these objects with A, B, and C according to the statement above.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.G.3.4 (Archived) | Estimate, select an appropriate tool, measure, and/or compute lengths to solve problems. Remarks: Activities do not include conversion of units. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.2.A.4.1 (Archived) | Extend number patterns to build a foundation for understanding multiples and factors – for example, skip counting by 2's, 5's, 10's. Remarks: Activities such as skip counting by 2's, 5's, and 10's will help students find multiples of 2, 5, and 10. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.A.4.2 (Archived) | Classify numbers as odd or even and explain why. Remarks: Example: Is 14 an even number or an odd number? Explain why. Provide manipulatives (e.g. color tiles, cubes) for students to explore even and odd numbers. 14 is an even number because 14 cubes form a rectangular array with a side of 2. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.A.4.3 (Archived) | Generalize numeric and non-numeric patterns using words and tables. Remarks: Activities include predicting numbers in a sequence when several terms are skipped. Example: Using the following number sequences, explain in words how you would know what the 9th number could be.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.2.A.4.4 (Archived) | Describe and apply equality to solve problems, such as in balancing situations. Remarks: Jorge made 3 identical apples balance with twelve 1-ounce weights. How much did each apple weigh? 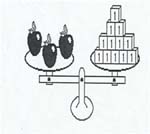 Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.2.A.4.5 (Archived) | Recognize and state rules for functions that use addition and subtraction. Remarks: Example: Using the numbers from the in and out chart, find and state the rule in words. What was the input number that gave 14?
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.2.G.5.1 (Archived) | Use geometric models to demonstrate the relationships between wholes and their parts as a foundation to fractions. Remarks: Example: Using pattern blocks, how many trapezoids does it take to make a hexagon? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.G.5.2 (Archived) | Identify time to the nearest hour and half hour. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.2.G.5.3 (Archived) | Identify, combine, and compare values of money in cents up to $1 and in dollars up to $100, working with a single unit of currency. Remarks: Name the different denominations of coins and bills. Match one coin of one denomination to an equivalent amount of another; in coins. Similarly, match dollar amounts of different denominations and combinations of bills. Activities will include the dollar sign ($) and cent (¢) symbols. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.2.G.5.4 (Archived) | Measure weight/mass and capacity/volume of objects. Include the use of the appropriate unit of measure and their abbreviations including cups, pints, quarts, gallons, ounces (oz), pounds (lbs), grams (g), kilograms (kg), milliliters (mL) and liters (L). Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.2.A.6.1 (Archived) | Solve problems that involve repeated addition. Remarks: Example: John earns $3 per day for 7 days. How much money did he earn? $3 + $3 + $3 + $3 + $3 + $3 +$3 = $21 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.3.A.1.1 (Archived) | Model multiplication and division including problems presented in context: repeated addition, multiplicative comparison, array, how many combinations, measurement, and partitioning. Remarks: Repeated addition: 4 bags of cookies with 8 in each bag. How many cookies are there? Multiplicative comparison: Sam has 8 baseball cards. Elise has 8 times as many. How many does Elise have? Array: A marching band has 8 rows with 7 students in each row. How many band members are marching? Combination: Patrick is getting dressed for school. He has 4 different colored shirts; blue, red, yellow and green. He has blue, tan and black shorts. How many combinations of a shirt and a pair of shorts can he make? Measurement: There are 35 bugs. You will put 5 bugs in each jar. How many jars will you need?
Partitive: You have 72 coins and 9 jars. If you want to place an equal number of coins in each jar, how many coins will you put in each jar? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.3.A.1.2 (Archived) | Solve multiplication and division fact problems by using strategies that result from applying number properties. Remarks: Remarks: The use of multiple strategies might incorporate number properties for both multiplication and division including the commutative property, associative property, distributive property, and the identity property. The zero property of multiplication may also be used to solve problems.
Example: Sally and Thomas each have a $5 bill and three $1 bills to spend at the book fair. Together the total amount of money they have can be shown using the expression below.
2 x (3 + 5)
Write a different expression that represents the total amount that Sally and Thomas have together. How much money do they have altogether?
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.3.A.1.3 (Archived) | Identify, describe, and apply division and multiplication as inverse operations. Remarks: Example: Twenty-four children are going to the circus in 6 cars. How many children can ride in each car, with the same number of children in each car? Which of the following number sentences can be used to solve this problem? a) 24 - 6 = __ b) 24 + 6 = __ c) __ ÷ 6 = 24 d) 6 x __ = 24 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.3.A.2.1 (Archived) | Represent fractions, including fractions greater than one, using area, set, and linear models. Remarks: Examples of area models include circular and rectangular shapes. Area models can also be represented by more unusual shapes. Examples of set models include groups of objects such as counters.
Linear models refer to the number line and fraction strips.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.3.A.2.2 (Archived) | Describe how the size of the fractional part is related to the number of equal sized pieces in the whole. Remarks: For instance, "As the number of equal parts increases, the size of each fractional part decreases." Fractions can also be compared by looking at numerators, such as when comparing 1/5 and 1/6. Since both fractions represent one part of a whole, the size of the parts can be compared. Fifths are larger than sixths so 1/5 is greater than 1/6. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.3.A.2.3 (Archived) | Compare and order fractions, including fractions greater than one, using models and strategies. Remarks: Strategies include using benchmark fractions and common numerators and denominators. Typical benchmarks for comparing fractions are 0, 1⁄2, and 1. Fractions can also be compared by looking at numerators, such as when comparing 2⁄5 and 2⁄6. Since both fractions represent two parts of a whole, the size of the parts can be compared. Fifths are larger than sixths so 2⁄5 is greater than 2⁄6. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.3.A.2.4 (Archived) | Use models to represent equivalent fractions, including fractions greater than 1, and identify representations of equivalence. Remarks: Example: Use your fraction circle set to come up with different combination of the same sized pieces that represent 1/2 of a circle.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.3.G.3.1 (Archived) | Describe, analyze, compare, and classify two-dimensional shapes using sides and angles - including acute, obtuse, and right angles - and connect these ideas to the definition of shapes. Remarks: Polygonal shapes can be classified by the number of sides. For example, quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides. Quadrilaterals can be further classified by other properties, such as the number of parallel pairs of sides (none, one pair or two pair). In the case of two pair of parallel sides, we call it a parallelogram. Note: Angles are classified by comparing them to a right angle as a benchmark. Students should be familiar with the geometric term "diagonal."
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.3.G.3.2 (Archived) | Compose, decompose, and transform polygons to make other polygons, including concave and convex polygons with three, four, five, six, eight, or ten sides. Remarks: Example: With pattern blocks, a trapezoid and a triangle can be combined to form a parallelogram or a large triangle. Also, the hexagon can be decomposed to form two trapezoids, and so forth.
Example: One can cut a triangle off of a parallelogram so that, when translated and attached to the other side, the parallelogram becomes a rectangle. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.3.G.3.3 (Archived) | Build, draw, and analyze two-dimensional shapes from several orientations in order to examine and apply congruence and symmetry. Remarks: Example: Draw a line of symmetry for each of the following: 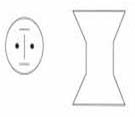  Symmetry mainly includes reflectional symmetry at grade 3. Students should explore that reflectional symmetry produces congruent shapes. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.3.A.4.1 (Archived) | Create, analyze, and represent patterns and relationships using words, variables, tables, and graphs. Remarks: Example: Look at the pattern below. Tell in your own words what shape is missing. Explain.  A possible answer would be a seven sided regular polygon because the number of side is increasing by one from left to right. Another possible answer is some polygon with pointy top because the pattern in the top of the shapes is pointy, flat, pointy, flat,...
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.3.G.5.1 (Archived) | Select appropriate units, strategies, and tools to solve problems involving perimeter. Remarks: Example: Find the perimeter of a football field.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.3.G.5.2 (Archived) | Measure objects using fractional parts of linear units such as 1/2, 1/4, and 1/10. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.3.G.5.3 (Archived) | Tell time to the nearest minute and to the nearest quarter hour, and determine the amount of time elapsed. Remarks: Elapsed time may include days, weeks, months, years, decades, and centuries. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.3.A.6.1 (Archived) | Represent, compute, estimate, and solve problems using numbers through hundred thousands. Remarks: Instructional focus should be placed on estimation through mental computation prior to written calculations. Students should be able to represent numbers with flexibility. For instance, 947 can be thought of as 9 hundreds 4 tens 7 ones, or as 94 tens 7 ones, or as 8 hundreds 14 tens 7 ones. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.3.A.6.2 (Archived) | Solve non-routine problems by making a table, chart ,or list and searching for patterns. Remarks: Example: A frog in a pit tries to go out. He jumps 3 steps up and then slides 1 step down. If the height of the pit is 21 steps, how many jumps does the frog need to make? Example: Show 5 different combinations of US coins that total 53¢. Example: The 24 chairs in the classroom are arranged in rows with the same number of chairs in each row. List all of the possible ways the chairs can be arranged. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.3.S.7.1 (Archived) | Construct and analyze frequency tables, bar graphs, pictographs, and line plots from data, including data collected through observations, surveys, and experiments. Remarks: Use of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of whole numbers should be included during this process.
At this grade level, students might analyze graphs with words such as most, least, minimum, and maximum to provide a conceptual foundation for the more formal terms such as mode and range that they will learn in later grades. The collected data and the intent of the data collection should help to determine the choice of data display.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.4.A.1.1 (Archived) | Use and describe various models for multiplication in problem-solving situations, and demonstrate recall of basic multiplication and related division facts with ease. Remarks: Given real-world problems and accompanying models that include equal-sized groups, arrays, area, and equal intervals on the number line, students should be able to give the multiplication or division basic fact associated with the situation. The goal is to develop quick recall of multiplication facts and related division facts.Basic multiplication facts include the factors 0 through 9. Related division facts include divisors 1 through 9 and dividends 0-81. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.A.1.2 (Archived) | Multiply multi-digit whole numbers through four digits fluently, demonstrating understanding of the standard algorithm, and checking for reasonableness of results, including solving real-world problems. Remarks: Place value and properties of operations and numbers should play major roles in developing strategies for multiplying multi-digit whole numbers. For example, 13 x 14 can be thought of as (10 + 3) x (10 + 4). The Distributive Property can then be applied along with focus on decomposition of numbers to multiply 10 x 10 and 10 x 4 then 3 x 10 and 3 x 4. These partial products are added to find the product of 13 x 14. This process should be connected to the standard algorithm.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.4.A.2.1 (Archived) | Use decimals through the thousandths place to name numbers between whole numbers. Remarks: Students may use a place value mat to represent decimal numbers through the thousandths with objects, write the symbolic representation with numerals, and name the decimal represented with words. Students can identify decimal numbers on a number line, write the symbolic representation with numerals, and name the decimal value with words. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.4.A.2.2 (Archived) | Describe decimals as an extension of the base-ten number system. Remarks: By fourth grade, students should know that the relationship between adjacent places in whole numbers is described by a ten-to-one rule (…, 1000, 100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01,...). This relationship should be developed for decimals. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.4.A.2.3 (Archived) | Relate equivalent fractions and decimals with and without models, including locations on a number line. Remarks: Students can explore equivalency of fractions and decimals by using rulers. Models may include rulers, fraction circles, sets of similar objects, and drawings. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.A.2.4 (Archived) | Compare and order decimals, and estimate fraction and decimal amounts in real-world problems. Remarks: Measurements (e.g., lengths) and dollar amounts provide useful contexts for estimating in the real world. Students should understand the relationships and equivalencies between decimals and fractions. . A decimal number may have an equivalent fraction- one where the denominator is (or can be) a power of 10, at this grade level 10, 100, or 1000. They should also be able to represent 5ths as decimals (for example, 3/5= 0.6) and halves as decimals (for example, 7 ½ = 7.5). Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.4.G.3.1 (Archived) | Describe and determine area as the number of same-sized units that cover a region in the plane, recognizing that a unit square is the standard unit for measuring area. Remarks: Geoboards, tiles, and grid paper provide helpful contexts for this exploration. The focus is on countable units rather than multiplying dimensions. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.G.3.2 (Archived) | Justify the formula for the area of the rectangle "area = base x height". Remarks: The students should be able to justify the formula for the area of the rectangle by explaining how counting units to find area of a rectangle is related to finding the area by multiplying. The idea of the area of a rectangle as "base x height" rather than "length x width" is useful in connecting to other area formulas.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.G.3.3 (Archived) | Select and use appropriate units, both customary and metric, strategies, and measuring tools to estimate and solve real-world area problems. Remarks: Students should recognize that the area of a piece of paper might be measured in square inches, the area of a room might be measured in square feet, and the area of a large piece of land might be measured in square miles. Alternately, these measurements might be in square centimeters, square meters, and square kilometers, respectively. Example: Students find the area of a composite shape. An L-shaped region may be decomposed into rectangular regions. Example: Find the area of the polygon in the picture. Explain or show how you found the area.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.4.A.4.1 (Archived) | Generate algebraic rules and use all four operations to describe patterns, including nonnumeric growing or repeating patterns. Remarks: Example 1: A number pattern is: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18... What is an algebraic rule to describe the nth number in the pattern? Example 2: The triangle below is shape 1 and the square is shape 2. This same pattern continues, in which each shape has one more side than the previous shape. How many sides would shape n have, where n can be any natural number? How do you know?
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.4.A.4.2 (Archived) | Describe mathematics relationships using expressions, equations, and visual representations. Remarks: Example: Mr. Sims has 168 oranges. He wants to pack them into boxes with 28 in each box. How many boxes does he need? Use pictures or diagrams to show what is happening in the problem. Record your solution with equations.
Example Alex is 4 years older than twice as old as Sam What expression gives Alex's age if you use the variable "S " to represent Sam's age? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.4.A.4.3 (Archived) | Recognize and write algebraic expressions for functions with two operations. Remarks: Regina received $50 from her grandmother as her birthday gift. Her grandfather told her that his Birthday gift will be to give her $5 each month, starting the month after her birthday. Regina decided to save her birthday gifts to buy her favorite music player. The table below illustrates the total amount of gift money that Regina will have received each month. Write an algebraic expression that can be used to show the total amount of money that Regina will have each month.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.4.G.5.1 (Archived) | Classify angles of two-dimensional shapes using benchmark angles (45°, 90°, 180°, and 360°) Remarks: Use pictures of real world objects or diagrams of shapes with angles and ask students to classify the given angles by using benchmark angles. Use protractor to draw the angles of 45, 90, 180, and 360 degrees.
Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.4.G.5.2 (Archived) | Identify and describe the results of translations, reflections, and rotations of 45, 90, 180, 270, and 360 degrees, including figures with line and rotational symmetry. Remarks: Paper folding, mirrors, and computer technology may be helpful in developing student understanding of these concepts. Simple tessellation of plane may provide engaging opportunities for practice. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.G.5.3 (Archived) | Identify and build a three-dimensional object from a two-dimensional representation of that object and vice versa. Remarks: Example: A cylinder is composed of 2 bases (circles) & a rectangle. A cube is composed of six squares. A sphere is not easily decomposed into basic two dimensional shapes. Provide nets for students to construct 3-dimensional objects. Challenge students to create their own nets using grid paper.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.4.A.6.1 (Archived) | Use and represent numbers through millions in various contexts, including estimation of relative sizes of amounts or distances. Remarks: Students should recognize the difference between distances such as 100 feet and 1,000 feet or 10 km and 200 cm. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.A.6.2 (Archived) | Use models to represent division as:
Remarks: The inverse of multiplication: 4 x 45 = 180, 180 ÷ 4 = 45, and 180 ÷ 45 = 4. Partitioning: We can share 180 things (possibly represented by base-ten blocks) evenly among 4 groups and determine the number of items in each group. Successive subtraction: We can find the quotient of 180 ÷45 by repeatedly subtracting 45 and counting the number of groups of 45 subtracted before reaching zero.
The area model is a useful model for exploring the inverse relationship between multiplication and division. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.A.6.3 (Archived) | Generate equivalent fractions and simplify fractions. Remarks: Earlier work with models of equivalent fractions in grade 3 should help students to develop conceptual understanding for the rules for generating equivalent fractions and simplifying fractions. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.A.6.4 (Archived) | Determine factors and multiples for specified whole numbers. Remarks: Multiples and factors should be explored as students determine common denominators for fractions. Use models to identify square numbers to 100.
Example: You have 28 chairs. Show all of the ways you can arrange these chairs into arrays. Draw the arrays. Record the dimensions of the arrays. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.A.6.5 (Archived) | Relate halves, fourths, tenths, and hundredths to decimals and percents. Remarks: Relate common fractions to equivalent decimals and percents such as: 1/4 = 0.25 = 25%. These representations should be related through both models and symbols. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.4.A.6.6 (Archived) | Estimate and describe reasonableness of estimates; determine the appropriateness of an estimate versus an exact answer. Remarks: An example in which an estimate is more appropriate than an exact answer is in estimating the amount of food needed for a party. You know the number of people you invited, but still you need to estimate the amount of food and drink to buy.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.5.A.1.1 (Archived) | Describe the process of finding quotients involving multi-digit dividends using models, place value, properties, and the relationship of division to multiplication. Remarks: Example of using models and place value: A student is representing 639÷3 using base ten blocks by dividing 639 into three equal groups; the student begins by placing 2 flats (2 hundreds blocks) in each group. What does that show about the quotient for 639÷3?
The Distributive Property is used when 639÷3 is addressed as (600 + 30 + 9) ÷ 3. Example of using the relationship of division to multiplication: Dividing 38 by 2, a student might notice that 2x20=40, and 38 is close to 40. 38 is 2 less than 40, so 38÷2 is 19. Another way to solve this division symbolically is as follows.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.1.2 (Archived) | Estimate quotients or calculate them mentally depending on the context and numbers involved. Remarks: Example: An appropriate estimate for the quotient, 286 ÷ 40 is 7 because 286 is close to 280 which is divisible by four and 280 ÷ 40 is 7 since 40 x 7 is 280. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.1.3 (Archived) | Interpret solutions to division situations including those with remainders depending on the context of the problem. Remarks: Example: 456 students and teachers are going on a field trip on buses. Buses can carry 52. How many buses do we need to take everyone on the filed trip? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.5.A.1.4 (Archived) | Divide multi-digit whole numbers fluently, including solving real-world problems, demonstrating understanding of the standard algorithm and checking the reasonableness of results. Remarks: Problem solving may include strategies using rounding and working backward. Example: Mary's school is going to visit a theme park. Mary is in charge of collecting money to buy tickets for her school. One ticket costs $75. Mary collected $ 33,900, but she does not know how many people gave her money. How many tickets can she buy with this money? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.5.A.2.1 (Archived) | Represent addition and subtraction of decimals and fractions with like and unlike denominators using models, place value, or properties. Remarks: Example: Joe and Anabel ordered pizza. Joe ate ½ of the pizza and Anabel ate 1/3 of the pizza. How much of the pizza was eaten and how much is left over? Fraction circles make a good model for this. To determine how much pizza was eaten altogether, a student may explain that the halves would each need to be split into 3 equal pieces (so that there would be 6 pieces all together) and the thirds would each need to be split into 2 equal pieces (so that there would be 6 pieces all together). Then 3/6 and 2/6 could be combined to see that altogether, 5/6 of the pizza was eaten. When students add 1.45 + 3.24, they should be encouraged to say "five hundredths and 4 hundredths are added to give 9 hundredths, etc." rather than "five plus 4 is 9, etc."
Models for adding and subtracting decimals may include base ten blocks and ten and hundred grids. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.2.2 (Archived) | Add and subtract fractions and decimals fluently, and verify the reasonableness of results, including in problem situations. Remarks: Example: Two friends share a candy bar that is divided into 12 equal sections. The first friend ate 1/2 of the candy bar. The second friend ate 1/3 of the candy bar. How much of the candy bar left? This is very similar to the situation in MA.5.A.2.1, but a rectangular model might be more appropriate. Students may use inverse operations to self-check sum/difference. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.2.3 (Archived) | Make reasonable estimates of fraction and decimal sums and differences, and use techniques for rounding. Remarks: Remarks: Use a variety of strategies for estimating sums and differences of fractions and decimals including benchmark fractions and decimals, and rounding techniques.
Example: Students know that 7/8 + 11/12 is close to 2, because 7/8 and 11/12 are each close to 1.
Example: Use appropriate benchmarks to estimate the difference between 1.801 and 1.239, be sure to show all work. Possible Answers: 1.75 – 1.25 = 0.5 OR 1 ¾ - 1 ¼ = ½
Example: Use an appropriate strategy to estimate the total cost for a shirt that costs $5.89 and a pair of shorts that costs $6.34, justify your answer. Possible Answers: If I round each of the cost to the nearest tenth, then $5.90 + $6.30 = $12.20. OR Since one costs slightly less than $6 and the other costs slightly more than $6, I would estimate the total cost to be 2 × $6 = $12. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.2.4 (Archived) | Determine the prime factorization of numbers. Remarks: Finding the least common multiple (LCM) and the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers is related to prime factorization.
Divisibility rules for numbers such as 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, and 10 may be explored. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.5.G.3.1 (Archived) | Analyze and compare the properties of two-dimensional figures and three-dimensional solids (polyhedra), including the number of edges, faces, vertices, and types of faces. Remarks: Example: Students use a geometric solid to see that a triangular prism is formed by congruent triangles on parallel planes connected by rectangles. Students draw nets, describe faces, count edges and count vertices and use this data as clues to name solids.
Example: Students build or draw models of 3-dimensional solids, and identify the characteristics and 2-dimensional components of 3-dimensional solids. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.5.G.3.2 (Archived) | Describe, define, and determine surface area and volume of prisms by using appropriate units and selecting strategies and tools. Remarks: Teachers should develop definitions by interpreting surface area as "covering all surfaces" or "wrapping with no gaps or overlaps" and volume as "filling". Example: Students find the total number of same-sized units of volume needed to fill a prism.
Example: Students recognize that the surface area of a cube is the sum of the areas of 6 square regions. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.5.A.4.1 (Archived) | Use the properties of equality to solve numerical and real world situations. Remarks: The properties of equality include: a) If you have a balanced situation, you can add, subtract, multiply or divide by the same number on both sides and the equality stays the same. b) If you have one quantity equal to another, you can substitute that quantity for the other in an equation. Examples: How much does a piece of cake weigh? How much does a coin weigh? Explain how you used properties of equality to determine your answer. 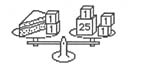  example: explain how to determine the answer to: 2+__=5+6 example: explain how to solve this equation for x: 3x + 5= 22 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.4.2 (Archived) | Construct and describe a graph showing continuous data, such as a graph of a quantity that changes over time. Remarks: In the 2007 Sunshine State Standards for mathematics, continuous line graphs are introduced for the first time in fifth grade. Students relate graphic displays to scenarios involving change over time and vice versa. Example: A bicycle rider starts riding and steadily increases his speed until he is riding 10 mph after 5 minutes. This means that he was riding 0 mph at 0 minutes, 2 mph after 1 minute, 4 mph after 2 minutes, and so forth. After he reaches 10mph, he rides at that rate for 8 minutes. Then he hits a tree and stops suddenly. Draw a graph of the rider's speed versus time during his ride. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.5.G.5.1 (Archived) | Identify and plot ordered pairs on the first quadrant of the coordinate plane. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.5.G.5.2 (Archived) | Compare, contrast, and convert units of measure within the same dimension (length, mass, or time) to solve problems. Remarks: Example: Convert 96 inches to the equivalent length measured in yards. 96 inches = Example: Convert 12.5 centimeters to millimeters. Students at this level are not expected to convert between different measurement systems. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.G.5.3 (Archived) | Solve problems requiring attention to approximation, selection of appropriate measuring tools, and precision of measurement. Remarks: Students recognize that a smaller unit provides a more precise measure and that precision is determined by the measure being used (for example, if using inches, you can measure to fractional parts of inches). Example: Find the measure of an angle using a protractor. Example: A student measures a table to the nearest foot and then measures the same table to the nearest inch to get a more precise measure.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.5.G.5.4 (Archived) | Derive and apply formulas for areas of parallelograms, triangles, and trapezoids from the area of a rectangle. Remarks: The formula for the area of a rectangle, "base x height", can be applied to develop formulas for the area of parallelograms, triangles, and trapezoids. Triangles can be constructed from diagonals of parallelograms to explore the formula "base x height divided by 2". Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.5.A.6.1 (Archived) | Identify and relate prime and composite numbers, factors, and multiples within the context of fractions. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.6.2 (Archived) | Use the order of operations to simplify expressions which include exponents and parentheses. Remarks: Students look for ( ) first, exponents second, multiplication and division from left to right third, and addition and subtraction from left to right fourth to simplify expressions. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.6.3 (Archived) | Describe real-world situations using positive and negative numbers. Remarks: Students may describe situations such as owing money or measuring elevations above and below sea level to explore negative numbers. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.6.4 (Archived) | Compare, order, and graph integers, including integers shown on a number line. Remarks: Students may explore negative and positive integers in science class through the following two science benchmarks: SC.5.P.8.1 and SC.5.P.9.1 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.5.A.6.5 (Archived) | Solve non-routine problems using various strategies including “solving a simpler problem” and “guess, check, and revise”. Remarks: Example: Give each student or pair 36 color tiles. Ask them how many different rectangles they can produce by using all the tiles. Students can use a small number of color tiles to find a pattern (finding the possible factors for the given number) and then apply that knowledge to 36 tiles. Example: Write all the whole numbers from 1 to 25 as addition of consecutive counting numbers. What observations do you have? Can you write every number this way? Be prepared to explain your strategy. [Some students might start with a number and look for consecutive counting numbers, others might start with combinations of consecutive counting numbers to add.]
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.5.S.7.1 (Archived) | Construct and analyze line graphs and double bar graphs. Remarks: Example: Students collect, display and analyze data based on their own investigations (for example, the amount of rainfall in a given month at a single or multiple locations). Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.5.S.7.2 (Archived) | Differentiate between continuous and discrete data, and determine ways to represent those using graphs and diagrams. Remarks: For instance, if growth of a plant over time is measured, the data is continuous because time is measured continuously and a line graph is appropriate. However, if the number of students present in the classroom per day is recorded, these data are discrete (countable) and a bar graph is appropriate.
Students may use a Venn Diagram to represent a data set. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.6.A.1.1 (Archived) | Explain and justify procedures for multiplying and dividing fractions and decimals. Remarks: For division of fractions, students might use drawings, manipulatives, and symbolic notation to describe how and explain why they can find a common denominator and then divide just the numerators to find the quotient. In the following fraction multiplication examples, students may use drawings or physical objects to represent the problems and explain their solution. Example 1: One-half of your yard is garden. One- fourth of your garden is a vegetable garden. What fraction of your yard is a vegetable garden? Draw a picture and write a number sentence that both describe the problem and solution. Pizza Parlor Scenarios Example 2: A cook made four pizzas that had 3/5 of a package of mushrooms on each. How many packages of mushrooms were used?
Example 3: Sue ate some pizza. 2/3 of a pizza is left over. Jim ate 3/4 of the left over pizza. How much of a whole pizza did Jim eat? Example 4: A party dessert pizza measures 2/3 of a yard by 3/4 of a yard. How much of a square yard is the party dessert pizza? Example 5: There was 4/5 of a pound of pizza dough leftover in the freezer from the previous day. The cook thawed out 3/8 of the leftover dough. How much of a pound of dough did the cook thaw?
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.A.1.2 (Archived) | Multiply and divide fractions and decimals efficiently. Remarks: Students may learn techniques such as mental math or specified algorithms to perform these operations. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.6.A.1.3 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems involving multiplication and division of fractions and decimals. Remarks: This standard includes finding the solution to multi-step problems.
Example: How many quarter-pound hamburgers can be made from 3 1/2 pounds of ground beef? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.6.A.2.1 (Archived) | Use reasoning about multiplication and division to solve ratio and rate problems. Remarks: Example: Four items cost $5.00 and all items are the same price. Explain how to find the cost for 9 items. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.6.A.2.2 (Archived) | Interpret and compare ratios and rates. Remarks: Example: Jessica made 8 out of 24 free throws. Bob made 5 out of 20 free throws. Who has the highest free throw ratio?
Ratios may be represented in various forms such as simple drawings or multiplication tables. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.6.A.3.1 (Archived) | Write and evaluate mathematical expressions that correspond to given situations. Remarks: Example: A plant is 3 cm high on Day 1. Each day after that the plant grows 2 cm taller. Assume that the plant grows at the same rate. Make a table and graph that show the height of the plant for Days 1 through 10. Write an expression to show the height on day n. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.A.3.2 (Archived) | Write, solve, and graph one- and two- step linear equations and inequalities. Remarks: The context should include patterns, models and relationships. Students should explore how "greater than or equal to" and strictly "greater than" are similar and different. A number line is a useful tool for modeling situations and inequalities such as "You have to be at least 40 inches tall to a ride roller coaster." and "x = 40".Graphing on coordinate plane is still limited to the first quadrant, but they can explore negative and positive integers on number line.
Example: The height of a tree was 7 inches in the year 2000. Each year the same tree grew an additional 10 inches. Write an equation to show the height h of the tree in y years. Let y be the number of years after the year 2000. Graph the height of the tree for the first 20 years. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.A.3.3 (Archived) | Work backward with two-step function rules to undo expressions. Remarks: Example: Sam set a function machine to multiply by 3, and then to add 4. He showed his chart to Wanda. How can Wanda find the missing input number?
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.A.3.4 (Archived) | Solve problems given a formula. Remarks: Example: The pressure exerted by a solid object on a solid surface can be calculated by using the formula, , where the variables P, F, and A represent pressure, force, and area respectively. A newly refinished wood floor can withstand a pressure of up to 40 pounds per square inch without sustaining damage. A 120 pound woman with high heels and a 240 pound man with flat heels each enter this room. Assume that at some point all of their weight is supported equally by the heels of both of their shoes. Given that each of the woman’s heels occupies an area of 0.25 in2 and each of the man’s heels occupies an area of 12 in2, find out each person’s potential for causing damage to the wood floor. Justify your answer. If a 15,000 pound African elephant with feet that each has an area of 100 in2 were to stand on this floor, would it cause damage to the floor? Explain your answer. Compare the three cases with each other. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.A.3.5 (Archived) | Apply the Commutative, Associative, and Distributive Properties to show that two expressions are equivalent. Remarks: Example: Is 7(m+2) the same as 7m + 2 or 7m + 14? Explain your choice. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.A.3.6 (Archived) | Construct and analyze tables, graphs, and equations to describe linear functions and other simple relations using both common language and algebraic notation. Remarks: Example 1: Each unicycle made needs 1 wheel. Explain why w=u where w is the number of wheels and u is the number of unicycles describes this relationship. Example 2: Each bicycle made needs 2 wheels. Explain why w=2b where w is the number of wheels and b is the number of bicycles describes this relationship. Example 3: Each tricycle made needs 3 wheels. Explain why w=3t where w is the number of wheels and t is the number of tricycles describes this relationship. Example 4: Below is a graph of the relationships in Examples 2 and 3. Explain why one of the lines is steeper than the other line.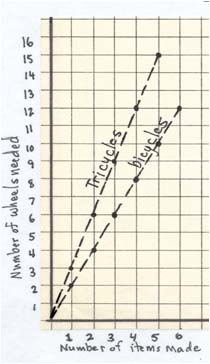 what would the graph of w=u look like? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.6.G.4.1 (Archived) | Understand the concept of Pi, know common estimates of Pi (3.14; 22/7) and use these values to estimate and calculate the circumference and the area of circles. Remarks: Using various circular objects, students determine that the ratio of circumference to diameter approximates the value of Pi. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.G.4.2 (Archived) | Find the perimeters and areas of composite two-dimensional figures, including non-rectangular figures (such as semicircles) using various strategies. Remarks: Example: Students see that the formula for the area of a circle is plausible by decomposing a circle into a number of wedges and rearranging them into shapes that approximates a parallelogram.
Example: Students might trace their foot on a piece of grid paper and use the full squares and the partial squares to estimate the area of the bottom of their foot. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.G.4.3 (Archived) | Determine a missing dimension of a plane figure or prism given its area or volume and some of the dimensions, or determine the area or volume given the dimensions. Remarks: Example: The volume of a rectangular prism is 112 cubic cm. The length is 7 cm, and the height is 8 cm. What is the depth of the prism?
Example: The figure below shows the floor of a living room. The rectangular part is covered with a carpet that covers a 22 square feet area. The house owner wants to cover the triangular part with carpet as well. Use the information provided in figure to determine the minimum additional carpet that will need to be purchased to cover the floor.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.6.A.5.1 (Archived) | Use equivalent forms of fractions, decimals, and percents to solve problems. Remarks: Example: John scored 75% on a test and Mary has 8 out of 12 correct on the same test. Each test item is worth the same amount of points. Who has the better score? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.A.5.2 (Archived) | Compare and order fractions, decimals, and percents, including finding their approximate location on a number line. Remarks: Example: Approximate the location of each of these values on a number line: 2/3, 0.57, and 0.575. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.6.A.5.3 (Archived) | Estimate the results of computations with fractions, decimals, and percents, and judge the reasonableness of the results. Remarks: Example: Amy bought 5 notebooks at $3.61 each. She estimated how much she needs to pay and gave the cashier $15. Is Amy's estimation appropriate? Explain your reasoning. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.6.S.6.1 (Archived) | Determine the measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variability (range) for a given set of data. Remarks: Students should make frequency tables for numerical or categorical data, grouping data in different ways to investigate how different groupings describe the data.
This is the first time in 2007 Florida mathematics standards that students are expected to use mean, median, mode, and range in a formal sense to describe a set of data. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.6.S.6.2 (Archived) | Select and analyze the measures of central tendency or variability to represent, describe, analyze, and/or summarize a data set for the purposes of answering questions appropriately. Remarks: A teacher can give students data sets that contain test/quiz grades for hypothetical classes. Students are asked to calculate and compare the class mean, median, mode, and range and discuss the effects of any outliers on the measures of central tendency. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.7.A.1.1 (Archived) | Distinguish between situations that are proportional or not proportional, and use proportions to solve problems. Remarks: Example 1: Two snakes, Moe and Joe, are each measured at two points in time. The first time, Moe is 3 inches long and Joe is 4 inches long. One year later, Moe is 5 inches long and Joe is 6 inches long. Which snake grew more? Maria believes that both snakes grew the same amount. Tom believes that Moe grew more. Explain under what circumstances either explanation could be correct. (In absolute terms they grew the same amount, which is not a proportional relationship; in relative terms one grew more than the other, which is a proportional relationship.)
Example 2: A recipe calls for 3 cups of flour and 2 eggs. If you wanted to increase the recipe and use 9 cups of flour, how many eggs would you need to use to keep the same ratio of flour to eggs? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.7.A.1.2 (Archived) | Solve percent problems, including problems involving discounts, simple interest, taxes, tips, and percents of increase or decrease. Remarks: Example: A merchant buys CDs for $11 wholesale and marks up the price by 35%. What is the retail price? Example: You are at a party with 100 people. 99% of the people are FSU fans. Some of the FSU fans left the party and now 98% of the people are FSU fans. How many people are still at the party? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.7.A.1.3 (Archived) | Solve problems involving similar figures. Remarks: Example: Rectangle A and rectangle B are similar. The lengths of congruent sides of rectangles A and B are 6 in. and 5 in., respectively. If the perimeter of rectangle A is 30 in., then what is the perimeter of rectangle B? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.7.A.1.4 (Archived) | Graph proportional relationships and identify the unit rate as the slope of the related linear function. Remarks: In a linear relation, the vertical change (change in y-value) per unit of horizontal change (change in x-value) is always the same and this ratio ("rise over run") is called the slope of the function.
Example: A babysitter earns $5 per hour. Draw a graph of money earned versus time. Find the numerical value of the slope and interpret it in words. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.7.A.1.5 (Archived) | Distinguish direct variation from other relationships, including inverse variation. Remarks: Direct variation between y and x is when y/x=k where k is a constant, or equivalently y=kx. Indirect variation is when xy=k where k is a constant, or equivalently y=k/x. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.7.A.1.6 (Archived) | Apply proportionality to measurement in multiple contexts, including scale drawings and constant speed. Remarks: The student might convert among different units of measurement to solve problems involving rates. Example 1: On a floor plan of your school, your classroom is 9 inches long and 6 inches wide. If the scale is 1 inch = 3 ft., what is the width of your classroom in feet? Explain your answer.
Example 2: You have a 4 in. by 5 in. photograph and you want to enlarge it to an 8 in. by 10 in. photograph. Roberto thinks that the new picture is four times as big as the old one. Dora thinks that the new picture is twice as big as the old one. Explain their thinking. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.7.G.2.1 (Archived) | Justify and apply formulas for surface area and volume of pyramids, prisms, cylinders, and cones. Remarks: Students should be limited to prisms, pyramids and cylinders when calculating surface area, and prisms, pyramids, cylinders and cones when calculating volume. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.7.G.2.2 (Archived) | Use formulas to find surface areas and volume of three-dimensional composite shapes. Remarks: This extends the work of grade 5 to using general formulas to compute the solutions for a variety of shapes.
The figure being composed or decomposed may include circles or parts of circles.
Example: Given a 3-Dimensional "E" shaped figure with labeled side lengths, find the surface area of the figure. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.7.A.3.2 (Archived) | Add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers, fractions, and terminating decimals, and perform exponential operations with rational bases and whole number exponents including solving problems in everyday contexts. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.7.A.3.3 (Archived) | Formulate and use different strategies to solve one-step and two-step linear equations, including equations with rational coefficients. Remarks: Example: It costs an initial fixed cost of $2 plus an additional $1.50 per mile to rent a taxi. Which equation represents the method for calculating the total cost of a taxi ride? What is the total cost for a 5-mile trip? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.7.A.3.4 (Archived) | Use the properties of equality to represent an equation in a different way and to show that two equations are equivalent in a given context. Remarks: Properties of equality explain the following results: · A balanced equation will remain balanced if you add, subtract, multiply or divide (excluding division by zero) both sides by the same number. · A quantity equivalent to another quantity can be substituted for it.
Example 1: What is another way to express the following equation? 3x + 14 = x + 30
Example 2: Why is 2x + 4 = x + 6 the same as 2x = x + 2 ?
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.7.G.4.1 (Archived) | Determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter, area, and volume of common geometric figures, and apply these relationships to solve problems. Remarks: See Example 2 in benchmark MA.7.A.1.6. The linear scale factor is 2. The areas of the two figures are related by a factor of 4 (2 squared). If this pattern was continued for a 3-dimensional figure, the volumes would be related by a factor of 8 (2 cubed). Students should encounter this concept in different contexts, and they should be encouraged to recognize the patterns themselves rather than be told about the relationship first.
Example: You have two circles with circumference pi and 4pi. What is the ratio of the areas of the circles? What is the ratio of the diameters? What is the ratio of the radii? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.7.G.4.2 (Archived) | Predict the results of transformations, and draw transformed figures with and without the coordinate plane. Remarks: Students should recognize that reflections, transformations, and rotations result in congruent figures. Other transformations (such as dilations) may not preserve congruency. Example 1: Draw the triangle with vertices (0,0), (3,0), (0,4). Translate (slide) the triangle 2 units to the right. What are the coordinates of the vertices of the new triangle?
Example 2: What happens to a figure drawn on a coordinate plane if each of its vertices' coordinates is multiplied by 2? What if they are multiplied by 1/4th? What about -2? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.7.G.4.3 (Archived) | Identify and plot ordered pairs in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Remarks: Quadrants 2, 3, and 4 are introduced for the first time in 7th grade. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.7.G.4.4 (Archived) | Compare, contrast, and convert units of measure between different measurement systems (US customary or metric (SI)), dimensions, and derived units to solve problems. Remarks: Example 1: You ride your bike from your house to the beach and home again. At the end of your trip, your bicycle odometer reads 8km. How many miles did you ride? Example 2: How many cm3 are in a 2-liter bottle of soda? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.7.A.5.1 (Archived) | Express rational numbers as terminating or repeating decimals. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.7.A.5.2 (Archived) | Solve non-routine problems by working backwards. Remarks: Solving non-routine problems involves creativity and critical thinking. Solution methods for non-routine problems are not prescribed. They may involve multiple representations, and are challenging for the learner. Example: Alex had some marbles. On his birthday, his father doubled the number of his marbles. Alex gave 5 marbles to his best friend. Then he divided the remaining marbles into three equal groups and shared them with his two brothers. Each brother got 11 marbles. What was the original number of marbles that Alex had before his birthday? Did he make a good choice of sharing his marbles? What strategy would you use if you were Alex?Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.7.S.6.1 (Archived) | Evaluate the reasonableness of a sample to determine the appropriateness of generalizations made about the population. Remarks: Example: You asked 10 of your classmates what is their favorite university in Florida. Five of them said Florida International University. Based on your sample, can we assume that FIU is the favorite university of approximately half of the students in your school? In your class? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.7.S.6.2 (Archived) | Construct and analyze histograms, stem-and-leaf plots, and circle graphs. Remarks: Students can represent the same data with different types of graphs and discuss the appropriateness of each graph based on the source of the data and the information required. An example of a stem-and-leaf plot for the data set (34, 30, 38, 42, 67, 68, 68, 56, 54, 34, 82, and 85) is as follows: Legend: 3| 234 means scores of 32, 33, and 34
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.7.P.7.1 (Archived) | Determine the outcome of an experiment and predict which events are likely or unlikely, and if the experiment is fair or unfair. Remarks: The student will represent probabilities as fractions and decimals between 0 and 1 (inclusive), and as percentages between 0% and 100% (inclusive), and verify that the probabilities are reasonable.
In 2007 mathematics standards, the concept of probability is introduced for the first time in 7th grade. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.7.P.7.2 (Archived) | Determine, compare, and make predictions based on experimental or theoretical probability of independent or dependent events, Remarks: Experiments could involve or not involve "replacement" of an event. Students must be able to distinguish between independent and dependent events. Example: Find the probability of choosing a red marble from a bag of 9 white marbles and 1 red marble, with or without replacement of each drawn marble. Students use manipulatives to obtain experimental results, compare results to mathematical expectations, and discuss the validity of the experiment.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.8.A.1.1 (Archived) | Create and interpret tables, graphs, and models to represent, analyze, and solve problems related to linear equations, including analysis of domain, range, and the difference between discrete and continuous data. Remarks: Example 1: Jan decided to save some money. She already had $25. She received and saved $5 on Friday each week for 8 weeks. Make a table and a graph of the money she would have each week. If she continues with this same savings plan, how much money will she have after 2 years? Is the situation in this problem continuous or discrete? The problem above is technically a discrete problem. A continuous linear function such as y=25+ 5x may be used to fit the data and to solve the problem. If the domain is integers, this is a discrete function. If the domain is all real numbers, this is a continuous function.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.8.A.1.2 (Archived) | Interpret the slope and the x- and y-intercepts when graphing a linear equation for a real-world problem. Remarks: Example: For the example 1in benchmark MA.8.A.1.1, graph the equation y = 5w + 25. Tell why the line "slopes up" by 5 each week. Also tell why the line crosses the y-axis at 25. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.8.A.1.3 (Archived) | Use tables, graphs, and models to represent, analyze, and solve real-world problems related to systems of linear equations. Remarks: Example 1: A zoo has turtles (each with four legs) and pelicans (each with two legs). There were 29 animals and 78 legs. How many of each type of animal were there? Your final solution should involve principles of equality. Example 2: The students in Mr. Kemp's class ordered T-shirts for the class. They found two different quotes for the cost of the shirts. Students should be encouraged to make tables, graphs, and equations and notice the interconnectedness of these representations.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.8.A.1.4 (Archived) | Identify the solution to a system of linear equations using graphs. Remarks: Remarks: Students should recognize that intersecting lines yield a unique solution; parallel lines yield no solution; and coincidental lines yield an infinite number of solutions. Students may use graphing technology to make observations about the effects of slope on the solution of systems of linear equations.
Example: Use a graph of the following functions to determine a solution to the system of equations. y = 5x + 3 y = 3x – 9 + 2x
Example: Jan started with $25 and saved $5 each week. Bill started at the same time with no money and saved $10 per week. Use a graph to determine if or when Bill and Jan will have the same amount of money. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.8.A.1.5 (Archived) | Translate among verbal, tabular, graphical, and algebraic representations of linear functions. Remarks: Example: Jan started with $25 and saved $5 each week. Bill started at the same time with no money and saved $10 per week. Make a table to display the data, write an equation to show the amount of money each person has each week, and graphically display the situation. Explain the relationship between different representations of the same data. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.8.A.1.6 (Archived) | Compare the graphs of linear and non-linear functions for real-world situations. Remarks: Students should understand that some situations can be modeled by a linear function and others cannot.
Example: Mark had $100 and added $10 to it each year. Mandy put $100 in the bank, earned 10% interest each year on her total amount of money in the bank, and left the interest in the bank account. Make a table of their money for 5 years. Graph the values. Explain why one function is linear and the other one is not. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.8.G.2.1 (Archived) | Use similar triangles to solve problems that include height and distances. Remarks: Example 1: At the same time a 10 ft flagpole casts an 8 ft shadow, a nearby tree casts a 40 ft shadow. How tall is the tree? Example 2: A 72-inch tall man casts a shadow that is 96 inches long. At the same time, a nearby crane casts a 52-foot long shadow. How tall is the crane? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.8.G.2.2 (Archived) | Classify and determine the measure of angles, including angles created when parallel lines are cut by transversals. Remarks: Students identify congruent angles, and unique pairings of angles that can be used to determine the measure of missing angles. Example 1: Given that lines k and l are parallel, determine which angles are vertical, complementary, supplementary, and corresponding.
 example 2: use a map of your town and ask students to identify vertical, complementary, supplementary, and right angles that are formed by the roads. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.8.G.2.3 (Archived) | Demonstrate that the sum of the angles in a triangle is 180-degrees and apply this fact to find unknown measure of angles and the sum of angles in polygons. Remarks: Example 1: "Make a paper triangle and cut off regions around the vertices. Then place the vertices together, meeting at a common point, to see that they form a (approximate) straight angle." Example 2: In the following diagram, line k is parallel to line l. Use properties of angles made when parallel lines are cut by transverse lines to demonstrate that the sum of the three interior angles of a planar triangle is 180 degrees.  Example 3: Determine the sum of the internal angles of a regular hexagon. Investigate whether this sum is the same or different for different hexagons. Explain your findings.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.8.G.2.4 (Archived) | Validate and apply Pythagorean Theorem to find distances in real world situations or between points in the coordinate plane. Remarks: Example 1: You are wrapping a gift for your teacher's birthday. It is a very long and skinny pencil. You want to wrap it in a box so that your teacher can not tell what shape it is. Your friend has a shoe box that measures 10 inches by 7 inches by 5 inches. The pencil is 13 inches long. Will you be able to fit the pencil into the shoe box and close the lid? Justify your answer with mathematics. Example 2: You are sailing your boat to Key West from Pensacola. Key West is 82°W and 25°N, and your boat is 84°W and 29°N. What is the distance from your boat to Key West? Assume 1° change in longitude or latitude is 70 miles.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.8.S.3.1 (Archived) | Select, organize and construct appropriate data displays, including box and whisker plots, scatter plots, and lines of best fit to convey information and make conjectures about possible relationships. Remarks: Example: Alfonso's bowling scores are 125, 142, 165, 138, 176, 102, 156, 130, and 142. Make a box-and-whiskers plot of the data. The box and whiskers plot below represents the bowling scores of Anna. Compare the bowling scores of Alfonso and Anna. Who is a better bowler? 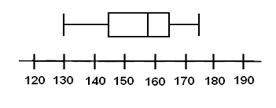
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.8.S.3.2 (Archived) | Determine and describe how changes in data values impact measures of central tendency. Remarks: Example: Mrs. Donohue has told her students that she will remove the lowest exam score for each student at the end of the grading period. Sara received grades of 43, 78, 84, 85, 88, 78, and 90 on her exams. What will be the different between the mean, median, and mode of her original grades and the mean, median, and mode of her five grades after Mrs. Donohue removes one grade?
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.8.A.4.1 (Archived) | Solve literal equations for a specified variable. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following equation for h: A=bh Example 2: The following equation tells you how much simple interest you will earn if you invest an amount of money (P) at a specified rate (r), for a given amount of time (t): I = Prt. Solve for P. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.8.A.4.2 (Archived) | Solve and graph one- and two-step inequalities in one variable. Remarks: Example: Solve the following inequality for x: 6x-3>10 . Graph the solution set. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.8.G.5.1 (Archived) | Compare, contrast, and convert units of measure between different measurement systems (US customary or metric (SI)) and dimensions including temperature, area, volume, and derived units to solve problems. Remarks: Example 1: Convert 25ºC to degrees Fahrenheit. Example 2: Convert 30 miles per hour to feet per second. 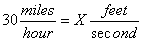 Students should not be using only formulas to do this. 1 mile = 5280 feet, and there are 3600 seconds in 1 hour. We may use these equivalencies to substitute feet for miles and seconds for hours.
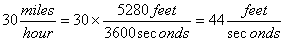 Another way to convert units is demonstrated here:
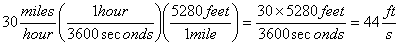 Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.8.A.6.1 (Archived) | Use exponents and scientific notation to write large and small numbers and vice versa and to solve problems. Remarks: Example 1: Write 3,600,000,000 in standard scientific notation. Example 2: Write 0.000 000 000 47 in standard scientific notation. Example 3: Write 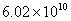 without the use of exponents. without the use of exponents.Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.8.A.6.2 (Archived) | Make reasonable approximations of square roots and mathematical expressions that include square roots, and use them to estimate solutions to problems and to compare mathematical expressions involving real numbers and radical expressions. Remarks: Example: The formula 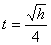 represents the time (t) in seconds that it takes an object to fall from a height of h feet. If a ball is dropped from a height of 200 ft, estimate how long it will take to reach the ground. represents the time (t) in seconds that it takes an object to fall from a height of h feet. If a ball is dropped from a height of 200 ft, estimate how long it will take to reach the ground.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.8.A.6.3 (Archived) | Simplify real number expressions using the laws of exponents. Remarks: Example 1: 32 · 33 = 3·3·3·3·3 = 35Example 2: Find the value of the expression 43 - 33.Example 3: Simplify the following expression:
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.8.A.6.4 (Archived) | Perform operations on real numbers (including integer exponents, radicals, percents, scientific notation, absolute value, rational numbers, and irrational numbers) using multi-step and real world problems. Remarks: Example 1: The table shows Mr. Smith's weight during the first 3 months of his diet. If he started his diet at 245 pounds, fill in the following table.
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.1.1 (Archived) | Know equivalent forms of real numbers (including integer exponents and radicals, percents, scientific notation, absolute value, rational numbers, irrational numbers).
Remarks: Example: Express 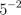 without an exponent. without an exponent.
Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.A.1.2 (Archived) | Compare real number expressions.
Remarks: Example 1: Which is greater: 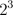 or or 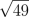 ? ? Example 2: Order the following numbers from the smallest to the largest: 3.2, 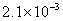 , , 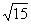 , -1. , -1.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.1.3 (Archived) | Simplify real number expressions using the laws of exponents. Remarks: Example 1: Simplify Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.A.1.4 (Archived) | Perform operations on real numbers (including integer exponents, radicals, percents, scientific notation, absolute value, rational numbers, irrational numbers) using multi-step and real-world problems.
Remarks: Example 1: If the length of one leg of a right triangle is 6 inches and the length of the hypotenuse is 10 inches, what is the length of the other leg? Example 2: Earth's volume is approximately 1.08×1012 km³. Sun's volume is approximately 1.41×1018 km³. How many times is the Sun larger than the Earth? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.1.5 (Archived) | Use dimensional (unit) analysis to perform conversions between units of measure, including rates. Remarks: Example 1: Convert 5 miles per hour to feet per second. Example 2: A sink is leaking 20 milliliters of water per second. How many gallons of water does it leak per day? Example 3: You bought an old car with a 442 cubic inch engine. Your friend has a 7.0 liter engine. Determine which engine is larger by converting 442 cubic inches to liters. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.1.6 (Archived) | Identify the real and imaginary parts of complex numbers and perform basic operations. Remarks: Example: Multiply (7-4i)(10+6i). Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.1.7 (Archived) | Represent complex numbers geometrically. Remarks: Example: Plot the point corresponding to 3 - 2i in the complex plane and determine the absolute value of this number. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.1.8 (Archived) | Use the zero product property of real numbers in a variety of contexts to identify solutions to equations. Remarks: Example 1: Solve for x. Example 2: Solve for x. Example 3: A ball is kicked and flies through the air according to the following function: h(t)= -16t^2+47t+3, where h is the height of the ball (in feet) and t is the number of seconds after the ball is kicked. At what time, t, does the ball hit the ground after being kicked? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.10.1 (Archived) | Use a variety of problem-solving strategies, such as drawing a diagram, making a chart, guessing- and-checking, solving a simpler problem, writing an equation, working backwards, and creating a table. Remarks: Students should work problems where they are required to distinguish relevant from irrelevant information, identify missing information, and either find missing data or make appropriate estimates. Example 2: The swimming pool at Roanoke Park is 24 feet long and 18 feet wide. The park district has determined that they have enough money to put a walkway of uniform width, with a maximum area of 288 square feet, around the pool. How could you find the maximum width of a new walkway? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.A.10.2 (Archived) | Decide whether a solution is reasonable in the context of the original situation. Remarks: Example 1: A student solving the equation 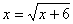 comes up with the solution set comes up with the solution set 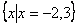 . Explain why . Explain why 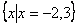 is not the solution set to this equation, and why the "check" step is essential in solving the equation. is not the solution set to this equation, and why the "check" step is essential in solving the equation.Example 2: A ball is kicked and flies through the air according to the following function: h(t)= -16t^2+47t+3, where h is the height of the ball (in feet) and t is the number of seconds after the ball is kicked. At what time, t, does the ball hit the ground after being kicked? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.10.3 (Archived) | Decide whether a given statement is always, sometimes, or never true (statements involving linear or quadratic expressions, equations, or inequalities, rational or radical expressions, or logarithmic or exponential functions).
Remarks: Example 1: Alex says x= -1 is the solution to the following system of inequalities. Explain to Alex when x=-1 is a solution and when it is not a solution.
Example 2: Is the statement Example 3: Let c be any constant number different than 5. Which of the following lines will always be parallel to y=2x+5? Explain your answer. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.A.10.4 (Archived) | Use counterexamples to show that statements are false. Remarks: Example 1: Show by an example that the following statement is false: "The product of two complex numbers is never a real number." Example 2: "All quadratic equations have exactly two distinct real roots." Provide a counter example to show that the statement in quotation marks is false. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.2.1 (Archived) | Create a graph to represent a real-world situation. Remarks: Example 1: Conduct an experiment as follows. Take a beverage out of a refrigerator and place it in a warm room. Measure its temperature every two minutes. Plot the temperature of the beverage as a function of time. What does the graph show about the temperature change of this beverage? Example 2: A child walks to school at a steady pace. Plot her distance from home as a function of time. Now plot her distance to the school as a function of time. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.2.2 (Archived) | Interpret a graph representing a real-world situation. Remarks: Example: Jessica is riding a bicycle in a straight line. The graph below shows her speed as it relates to the time she has spent riding. Assign appropriate units to the labels of the axes and insert numbers to the axes. Describe what might have happened to account for this graph.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.2.3 (Archived) | Describe the concept of a function, use function notation, determine whether a given relation is a function, and link equations to functions. Remarks: Example 1: Given the relation {(-3, -1), (2, -1), (1, 0), (2, 5)}, determine if the relation can be a function. Example 2: for f(x)=2x+6, find f(3) and find x such that f(x)=10 Example 3: Given the graph of the relation below, decide if this relation is a function. Explain your reasoning.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.2.4 (Archived) | Determine the domain and range of a relation. Remarks: Example: Determine the domain and range of 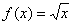 so that f(x) is a function. so that f(x) is a function.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.2.5 (Archived) | Graph absolute value equations and inequalities in two variables. Remarks: Example: Draw the graph of y = |2x - 5| and compare it with the graph of y = 2x - 5. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.2.6 (Archived) | Identify and graph common functions (including but not limited to linear, rational, quadratic, cubic, radical, absolute value). Remarks: Example: Graph 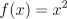 , , 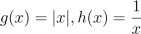 and and 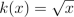 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.2.7 (Archived) | Perform operations (addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication) of functions algebraically, numerically, and graphically.
Remarks: Example: Let f(x)=7x+2 and g(x)=x². Find f(x)*g(x) Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.2.8 (Archived) | Determine the composition of functions. Remarks: Example: Let f(x)=x³ and g(x)=x-2. Find f(g(5)) and g(f(x)) Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.A.2.9 (Archived) | Recognize, interpret, and graph functions defined piece-wise with and without technology.
Remarks: Example: Sketch the graph of 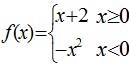 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.2.10 (Archived) | Describe and graph transformations of functions
Remarks: Example: Describe how you would graph 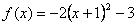 from the graph of from the graph of 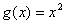 . .
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.2.11 (Archived) | Solve problems involving functions and their inverses. Remarks: Example: Find the inverse of the f(x)=x³-1 function. Sketch the graph of the function and its inverse Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.A.2.12 (Archived) | Solve problems using direct, inverse, and joint variations. Remarks: Example 1: According to Hooke's Law, the force needed to stretch a spring is directly proportional to the net spring stretch (stretched spring length minus original spring length). If 20 Newtons (N) force results in a net spring stretch of 5 centimeters, what is the net spring stretch achieved when a force of 80N is applied (assuming 80N force does not exceed the spring's stretch limit)? Example 2: On Monday, your drive to work takes 10 minutes and your average speed is 30 mph. On Tuesday, your drive on the same route takes 15 minutes. What is your average speed on Tuesday? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.A.2.13 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems involving relations and functions. Remarks: Example 1: You and your parents are going to Boston. You will rent a car at Boston's Logan International Airport on a Monday morning and drop the car off in downtown Providence, RI, on the following Wednesday afternoon. Find the rates from two national car companies and plot the costs on a graph. You may choose limited or unlimited mileage plans. Decide which company offers the best deal. Explain your answer. Example 2: A cab company charges a fixed flag rate of $20 and $1.40 for every mile covered. Write an expression for the total cab fare as a function of distance driven. Then solve for the total fare after the cab traveled for 36 miles. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.3.1 (Archived) | Solve linear equations in one variable that include simplifying algebraic expressions. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following equation for x: 3(2x+5) = 10x-3+2x Example 2: Solve the following equation for m: ½m + 2(¾m-1)=¼m+6 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.2 (Archived) | Identify and apply the distributive, associative, and commutative properties of real numbers and the properties of equality. Remarks: Example 1: Simplify the following expresion and identify the properities used in each step: 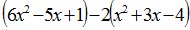 example 2: given the following solution identify the properties used to justify each step: 3x+7=2x+1+3x 3x+7=2x + 3x+1 3x+7=5x+1 -2x=-6 x=3 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.3 (Archived) | Solve literal equations for a specified variable. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following equation for p: q=4p-11. Example 2: Solve the following equation for c: ac=2b + 2c Example 3: The area formula for a circle is: A = p r2. Solve for r.. Solve for . Example 4: The following formula tells you how to convert degrees in Celsius to degrees in Fahrenheit: Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.4 (Archived) | Solve and graph simple and compound inequalities in one variable and be able to justify each step in a solution. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following inequality for x and then graph the solution set on a number line: 7<3x+5<11 Example 2: Solve the following inequality for x in the set {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}: 6x-3>10 Show your work. Example 3: Solve the following inequality for x, explaining each step in your solution: 8x-7≤2x+5 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.5 (Archived) | Symbolically represent and solve multi-step and real-world applications that involve linear equations and inequalities. Remarks: Example 1: You are selling tickets for a play that cost $3 each. You want to sell at least $50 worth. Write and solve an inequality for the minimum number of tickets you must sell. Example 2: An alloy is a metal that contains combinations of different types of metal. A manufacturing company needs to make an alloy that has nickel content between 43% and 47% (based on mass). The company already has an alloy with 50% nickel and another alloy with 40% nickel. They plan to mix them to make the alloy they need. Find the least and greatest mass (in kg) of a 50% nickel alloy that should be mixed with a 40% nickel alloy to end up with 100 kilograms of an alloy containing the required percentage of nickel.
|
| MA.912.A.3.6 (Archived) | Solve and graph the solutions of absolute value equations and inequalities with one variable. Remarks: Example 1: Given the following equation, solve for x and graph the solution on a number line: |2x=5|=7 Example 2: Given the following inequality, solve for x and graph the solution on a number line: |3x-2|≥5 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.3.7 (Archived) | Rewrite equations of a line into slope-intercept form and standard form. Remarks: Example 1: Write the following linear equation in standard form 6y = 12 - 5x. Example 2: Write the equation of the line 4x + 3y = 12 in slope-intercept form. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.A.3.8 (Archived) | Graph a line given any of the following information: a table of values, the x- and y-intercepts, two points, the slope and a point, the equation of the line in slope-intercept form, standard form, or point-slope form . Remarks: Example 1: Graph the equation 3x - y = 2. Example 2: Graph the equation y = ½ x + 2 Example 3: Graph the line that contains (3,0) and has a slope of -3/2. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.9 (Archived) | Determine the slope, x-intercept, and y-intercept of a line given its graph, its equation, or two points on the line. Remarks: Example: Find the slope and y-intercept of the line described by the equation 4x + 6y = 9. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.10 (Archived) | Write an equation of a line given any of the following information: two points on the line, its slope and one point on the line, or its graph. Also, find an equation of a new line parallel to a given line, or perpendicular to a given line, through a given point on the new line. Remarks: Example 1: Find an equation of the line through the points (1, 4) and (3, 10). Example 2: Find an equation of the line that goes through the point (5, -2) with a slope of -2 Example 3: Find an equation of the line through the point (1, 4) and perpendicular to y = 3x + 1. Example 4: Find an equation of the line parallel to y = 3x + 2 that passes through the origin. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.11 (Archived) | Write an equation of a line that models a data set, and use the equation or the graph to make predictions. Describe the slope of the line in terms of the data, recognizing that the slope is the rate of change. Remarks: Example 1: As your family is traveling along an interstate, record the odometer reading every 5 minutes. See if a graph of time and distance shows that the relation is approximately linear. If so, write the equation of the line that best fits your data. Predict the time for a journey of 50 miles. What does the slope of the line represent?
Example 2: You light a candle and record its height in centimeters every minute. The results recorded as (time, height) are (0, 20), (1, 18), (2, 16), (3, 14), (4, 13), (5, 11), (6, 10), (7, 8), (9, 4), and (10, 3). Find the line of best fit to express the candle's height as a function of the time and state the meaning of the slope in terms of the burning candle.
|
| MA.912.A.3.12 (Archived) | Graph a linear equation or inequality in two variables with and without graphing technology. Write an equation or inequality represented by a given graph. Remarks: Example: On a coordinate plane, graph of the following inequality: 3x+8y≥24 Example: Use a spreadsheet to create a line graph of the following function: y = (3/4)x + 7 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.13 (Archived) | Use a graph to approximate the solution of a system of linear equations or inequalities in two variables with and without technology. Remarks: Example 1: Graph 3y - x = 0 and 2x + 4y = 15 on the same coordinate system. Determine whether the lines intersect. If so, find the point of intersection. Example 2: Graph the following inequalities and shade the region (if any) on the coordinate plane where both inequalities are true: y ≤ 4 and x + y ≤ 5 Example 3: Approximate the solution, if any, for the following system of linear equations:
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.14 (Archived) | Solve systems of linear equations and inequalities in two and three variables using graphical, substitution, and elimination methods. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following system of equations by substitution: 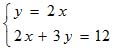 Example 2: Graph the solution for the following system of inequalities: 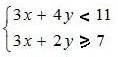 Example 3: Solve the following system of equations: 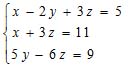 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.3.15 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems involving systems of linear equations and inequalities in two and three variables. Remarks: Example 1: Each week, you work a total of 20 hours. Some of the 20 hours is spent working at the local bookstore and some spent at the drugstore. You prefer the bookstore and want to work at least 10 more hours at the bookstore relative to the drugstore. Draw a graph to show the possible combinations of hours that you could work. Example 2: Let x = the amount of liquid (in milliliters) of a product sold by some company. The income (I) that the company makes from sales of the liquid can be represented by the equation I(x)=10.5x and the expenses (E) for the production of the liquid can be represented by the equation E(x)=5.25x+10,000, where I and E are in dollars. What is the minimum amount of the liquid (in milliliters) that the company must sell to reach the break-even point (the point where income in dollars is equal to expenses in dollars)? Example 3: You need to rent a car to drive from Pensacola to Key West. You will need the car for 7 days. One car rental agency charges $55 per day and $0.06 per mile. Another rental agency charges $65 per day with unlimited mileage. Which rental offer will cost you less? Create a situation where the rental offer in this situation will cost more than the other offer. Explain. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.4.1 (Archived) | Simplify monomials and monomial expressions using the laws of integral exponents. Remarks: Example 1: Simplify 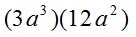 Example 2: Simplify: 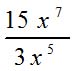 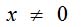 Example 3: Simplify: 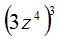 Example 4: Simplify: 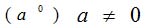 Example 5: Simplify: 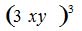 Example 6: Simplify: 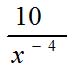 Example 7: Simplify: 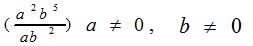 Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.A.4.2 (Archived) | Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. Remarks: Example 1: 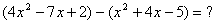 example 2: (n+2)(4n-5)=? Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.A.4.3 (Archived) | Factor polynomial expressions. Remarks: Example 1: Factor 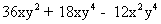 Example 2: Factor 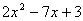 Example 3: Factor 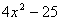 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.4.4 (Archived) | Divide polynomials by monomials and polynomials with various techniques, including synthetic division. Remarks: 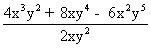 Example 1: Simplify Example 1: SimplifyExample 2: 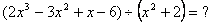 Example 3: Use synthetic division to divide 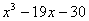 by x+3. by x+3.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.4.5 (Archived) | Graph polynomial functions with and without technology and describe end behavior.
Remarks: End behavior may be interpreted as behavior of the function for very large positive or negative(absolutely) independent variables. Example 1: Graph the following equation: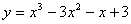 Example 2: Describe the end behavior for the graph of the following equation 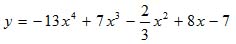
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.4.6 (Archived) | Use theorems of polynomial behavior (including but not limited to the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, Remainder Theorem, the Rational Root Theorem, Descartes' Rule of Signs, and the Conjugate Root Theorem) to find the zeros of a polynomial function.
Remarks: Example 1: Given that 4 is a zero of the polynomial 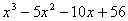 , use synthetic divison to find the remaining zeros of the polynomial. , use synthetic divison to find the remaining zeros of the polynomial.Example 2: Use the Remainder Theorem to evaluate 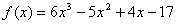 at x=3. Explain your solution method. at x=3. Explain your solution method. Example 3: Use the Rational Root Theorem to determine the possible rational roots of the equation 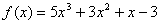
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.4.7 (Archived) | Write a polynomial equation for a given set of real and/or complex roots. Remarks: Example: Find a polynomial equation with the lowest degree possible and with real coefficients that involves the following three roots:
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.4.8 (Archived) | Describe the relationships among the solutions of an equation, the zeros of a function, the x-intercepts of a graph, and the factors of a polynomial expression with and without technology.
Remarks: Example: Use technology to find the solutions of the following equation: 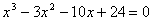 . Relate your results to the graph of the function . Relate your results to the graph of the function 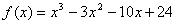
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.4.9 (Archived) | Use graphing technology to find approximate solutions for polynomial equations. Remarks: Example: Approximate the solution(s) of 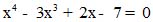 to the nearest thousandth. to the nearest thousandth.Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.A.4.10 (Archived) | Use polynomial equations to solve real-world problems. Remarks: Example: You want to make an open-top box with a volume of 500 square inches from a piece of cardboard that is 25 inches by 15 inches by cutting squares from the corners and folding up the sides. Find the possible dimensions of the box. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.4.11 (Archived) | Solve a polynomial inequality by examining the graph with and without the use of technology.
Remarks: Example: Find the solution for 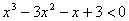 by graphing the function by graphing the function 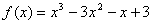 . .
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.4.12 (Archived) | Apply the Binomial Theorem.
Remarks: Pascal's triangle is a relevant and interesting structure for examining the Binomial Theorem. Students are expected to know how to use Pascal's triangle in expanding binomials raised to positive integer powers. Example: Expand 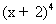
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.5.1 (Archived) | Simplify algebraic ratios. Remarks: Example: Simplify 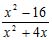 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.5.2 (Archived) | Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions.
Remarks: Example: Find the sum of 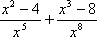 , and tell for what value(s) of x the sum is undefined. , and tell for what value(s) of x the sum is undefined.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.5.3 (Archived) | Simplify complex fractions. Remarks: Example: Simplify 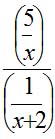 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.5.4 (Archived) | Solve algebraic proportions. Remarks: Example: Create a tutorial to be posted to the school's Web site to explain how to solve an algebraic proportion for beginning Algebra students. Use 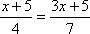 as an example. as an example.Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.A.5.5 (Archived) | Solve rational equations. Remarks: Example: Solve the following rational equation for n: 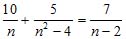 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.5.6 (Archived) | Identify removable and non-removable discontinuities, and vertical, horizontal, and oblique asymptotes of a graph of a rational function, find the zeros, and graph the function. Remarks: Example: Identify vertical, horizontal, and oblique asymptotes, find the zeros, and graph the following rational functions: 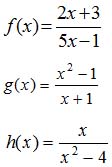 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.5.7 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems involving rational equations (mixture, distance, work, interest, and ratio). Remarks: Example: It takes Bob 3 hours to paint one side of a house. It takes Joe 2 hours to paint the same side of the house. How long will it take them if they work together? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.6.1 (Archived) | Simplify radical expressions Remarks: Example 1: Simplify 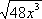 Example 2: Simplify 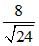 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.6.2 (Archived) | Add, subtract, multiply, and divide radical expressions (square roots and higher). Remarks: Example 1: Simplify 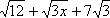 Example 2: Simplify 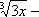 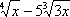 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.6.3 (Archived) | Simplify expressions using properties of rational exponents. Remarks: Example 1: Simplify 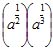 Example 2: Simplify 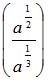 Example 3: Simplify 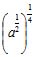 Example 4: Simplify 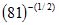 Example 5: Simplify 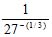 Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.A.6.4 (Archived) | Convert between rational exponent and radical forms of expressions. Remarks: Example 1: Rewrite 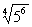 as 5 to a rational power. as 5 to a rational power. Example 2: Rewrite 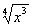 as x to a rational power. as x to a rational power.
Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.A.6.5 (Archived) | Solve equations that contain radical expressions. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following equation for x: 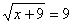 Example 2: Solve the following equation for y: 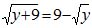 Example 3: Solve the following equation for z: 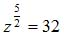 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.7.1 (Archived) | Graph quadratic equations with and without graphing technology. Remarks: Example 1: Draw the graph of 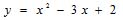 using a graphing calculator or a spreadsheet (generate a data set), display the graph to check your work. using a graphing calculator or a spreadsheet (generate a data set), display the graph to check your work.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.7.2 (Archived) | Solve quadratic equations over the real numbers by factoring and by using the quadratic formula. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following equation for x: x² - 3x + 2=0 Example 2: Solve the following equation for x: x² - 7x + 9=0 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.7.3 (Archived) | Solve quadratic equations over the real numbers by completing the square. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following equation for x: 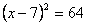 Example 2: Solve the following equation for x by completing the square: 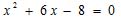 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.7.4 (Archived) | Use the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation. Remarks: Example: Use the discriminant to determine whether 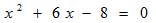 has distinct real roots. has distinct real roots.Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.A.7.5 (Archived) | Solve quadratic equations over the complex number system. Remarks: Example: Solve the following equation for x over the set of complex numbers: 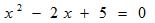 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.7.6 (Archived) | Identify the axis of symmetry, vertex, domain, range and intercept(s) for a given parabola. Remarks: Example: Identify the axis of symmetry, vertex, domain, range, and intercepts for the graph of 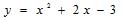 Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.A.7.7 (Archived) | Solve non-linear systems of equations with and without using technology. Remarks: Example: Find the solution for the following system of equations: 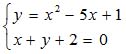 Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.A.7.8 (Archived) | Use quadratic equations to solve real-world problems. Remarks: Example: You have just planted a rectangular garden of corn in a plot near your home. You want to plant a uniform border of carrots around the rows of corn as shown in the figure below. According to the amount of seeds you have, you need an equal amount of area for corn and carrots. What should the width, x, in feet, of the border be?
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.A.7.9 (Archived) | Solve optimization problems. Remarks: Example: You have 100 feet of fencing to make three sides of a rectangular area using an existing straight fence as the fourth side. Construct a formula in a spreadsheet to determine the area you can enclose. Use the spreadsheet to make a conjecture about the maximum area possible. Prove (or disprove) your conjecture by solving an appropriate quadratic equation. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.A.7.10 (Archived) | Use graphing technology to find approximate solutions of quadratic equations. Remarks: Example: Use a graphing calculator to solve the following equation for x to the nearest tenth: 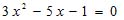 Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.8.1 (Archived) | Define exponential and logarithmic functions and determine their relationship Remarks: Example: Find the inverse of 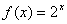 . Identify the domain and range of . Identify the domain and range of 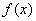 and and 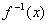 . .Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.8.2 (Archived) | Define and use the properties of logarithms to simplify logarithmic expressions and to find their approximate values. Remarks: Example 1: Evaluate the following expression: 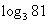 Example 2: Simplify 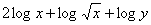 . .Example 3: Find the value of 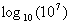 Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.A.8.3 (Archived) | Graph exponential and logarithmic functions. Remarks: Example 1: Draw the graphs of the functions 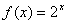 and and 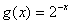 . Explain their differences and similarities. . Explain their differences and similarities.Example 2: Draw the graphs of the functions 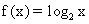 and and 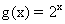 and describe their relationship. and describe their relationship.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.8.4 (Archived) | Prove laws of logarithms. Remarks: Example: Use the fact that 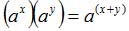 to show that to show that 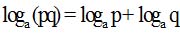 Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.A.8.5 (Archived) | Solve logarithmic and exponential equations. Remarks: Example 1: Solve the following equation for x: Example 2: Solve the following equation for t:
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.8.6 (Archived) | Use the change of base formula. Remarks: Example: Write 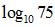 as a logarithm of base 2. as a logarithm of base 2.Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.A.8.7 (Archived) | Solve applications of exponential growth and decay. Remarks: Example: The population of a certain country can be modeled by the equation 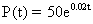 , where P(t) is the population in millions and t is the number of years after 1900. Find when the population is 100 million, 200 million, and 400 million. What do you notice about these time periods? , where P(t) is the population in millions and t is the number of years after 1900. Find when the population is 100 million, 200 million, and 400 million. What do you notice about these time periods?Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.A.9.1 (Archived) | Write the equations of conic sections in standard form and general form, in order to identify the conic section and to find its geometric properties (foci, asymptotes, eccentricity, etc.). Remarks: Example 1: Write the following equation in standard form: Example 2: Write the following equation in standard form: Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.9.2 (Archived) | Graph conic sections with and without using graphing technology. Remarks: Example: Graph the following conic sections: 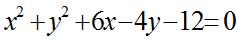 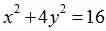 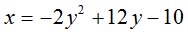 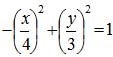 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.A.9.3 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems involving conic sections Remarks: Example: The planet Earth orbits the Sun elliptically, with the sun as one of the foci. Given that the length of the major axis of this ellipse is approximately 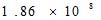 miles and the eccentricity of the ellipse is about 0.0167, find the smallest distance and the largest distance of earth from the sun. miles and the eccentricity of the ellipse is about 0.0167, find the smallest distance and the largest distance of earth from the sun.Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.1.1 (Archived) | Use recursive and iterative thinking to solve problems, including identification of patterns, population growth and decline, and compound interest. Remarks: Example 1: How many handshakes would occur in this room if everyone shook hands with everyone else? Create a spreadsheet that will find the number of handshakes starting with one person and increasing the number to 15. Example 2: Mary has $1000 at the beginning of 2008. She is going to invest all that money plus $600 every year from now in a certain account that brings in an annual yield of 6.8%. Assume that the interest rate is stable. Let B0 represents the initial money, B1 represents the amount of money at the end of 2008 (year1), B2 represents the amount of money at the end of 2009 (year2), and so on. Write a recursive function to find out Mary’s money at the end of any given year (year n). Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.1.2 (Archived) | Use finite differences to solve problems and to find explicit formulas for recurrence relations. Remarks: Example: Given the set of points {(1,-3), (2.2), (3,13), (4,30), (5,53) }use the method of finite differences to find a polynomial expression that generates these points. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.D.1.3 (Archived) | Use mathematical induction to prove various concepts in number theory (such as sums of infinite integer series, divisibility statements, and parity statements), recurrence relations, and other applications. Remarks: Example 1: Prove that the sum of the first n odd positive integers is n2. Example 2: Prove that 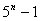 is divisible by 4 for n≥1 and n is integer. is divisible by 4 for n≥1 and n is integer. Example 3: Prove that for every integer n≥1, 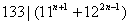 . .Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.10.1 (Archived) | Sketch the graph of a curve in the plane represented parametrically, indicating the direction of motion. Remarks: Example: Sketch the graph of the curve with parametric equations x=5-3t, y=-2 + t, and indicate the direction of motion as t increases. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.10.2 (Archived) | Convert from a parametric representation of a plane curve to a rectangular equation and vice-versa.
Remarks: Example 1: A curve has parametric representation 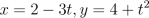 . Find an equation for the curve in rectangular coordinates. . Find an equation for the curve in rectangular coordinates. Example 2: Find a parametric representation for the ellipse with the rectangular equation 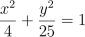 . .Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.D.10.3 (Archived) | Use parametric equations to model applications of motion in the plane. Remarks: Example: Suppose an object moving at constant velocity is at the point A(5,3) when time t=0 seconds, and at point B(-4, 15) when t=3 seconds. Find the velocity and speed of the object, and parametric equations for the motion of the object. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.11.1 (Archived) | Define arithmetic and geometric sequences and series. Remarks: Example: An investment doubles each decade. If the principal was $1000.00, write the sequence that shows the amount for each of four decades. Is this sequence arithmetic or geometric? Why? Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.D.11.2 (Archived) | Use sigma notation to describe series. Remarks: Example: Using the sigma notation, describe the total area of a set of 12 rectangles. Each of the rectangles has a width of 2 units. The first has a height of 5 units and the height of each successive rectangle is 2 units more than the previous one. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.D.11.3 (Archived) | Find specified terms of arithmetic and geometric sequences. Remarks: Example: A decorative brick wall is designed with one brick on the top row and each row below the top containing two more bricks than the row above. How many bricks are in the 20th row? Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.D.11.4 (Archived) | Find partial sums of arithmetic and geometric series, and find sums of infinite convergent geometric series. Use Sigma notation where applicable. Remarks: Example 1: A decorative brick wall is designed with one brick on the top row and each row below the top containing two more bricks than the row above. How many bricks are needed to make the wall 50 rows high? Example 2: A ball is dropped from a height of 6 feet. It bounces back up to a height of 4 feet, falls back to the ground and continues bouncing. If each bounce is 2/3 the height of the previous bounce, find the total vertical distance traveled by the ball. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.11.5 (Archived) | Explore and use other sequences found in nature such as the Fibonacci sequence and the golden ratio. Remarks: Example: Determine the first ten terms of the Fibonacci sequence. Calculate the ratio of the two adjacent terms such as the ratio of the second term to the first term, third term to the second term, fourth term to the third term, and so on. What would happen to the ratio between two adjacent terms as the sequence proceeds? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.2.1 (Archived) | Use Euler and Hamilton cycles and paths in graphs to solve routing problems. Remarks: Example 1: There are two islands in the River Seine in Paris. The city wants to construct four bridges that connect each island to each side of the riverbank and one bridge that connects the two islands directly. The city planners want to know if it is possible to start at one point, cross all five bridges, and end up at the same point without crossing a bridge twice. Use a graph to help solve this problem. Explain your answer. Example 2: A city planner is planning a bus route. She drew the following route, where each vertex represents a bus stop. She wants to make sure that the bus starts from the terminal, vertex a, travels all the roads exactly once and returns back to the terminal. Is this possible? If not, add additional bus stops (vertices) or roads (edges) to make it possible. What is your strategy?  Example 3: A sales person needs to travel to each city shown on the following graph. He wants to start at city a, visit each city exactly one time, and then return to the initial city (city a). Is this possible? If yes, find such a cycle for him.  Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.D.2.2 (Archived) | Use critical path analysis to solve scheduling problems. Remarks: Example: Write a critical task list for redecorating your room. Some tasks depend on the completion of others and some may be carried out at any time. Use a graph to find the least amount of time needed to complete your project. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.D.2.3 (Archived) | Use graph coloring techniques to solve problems. Remarks: Example: Color a map of the counties of the State of Florida so that no adjacent counties are the same color. What is the minimum number of colors needed? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.2.4 (Archived) | Use spanning trees, rooted trees, binary trees, and decision trees to solve problems. Remarks: Example 1: Suppose that you need to identify a fake coin among 8 coins by using a pan balance. The fake coin is lighter than the other seven coins that all weigh the same. What is the minimum number of weighing needed to guarantee that the fake coin is found? Make a decision tree to represent your solution. Solve the same problem by assuming that the fake coin is either lighter or heavier than the other seven coins. Example 2: Suppose that you will have a single elimination chess tournament in your classroom. Draw the graph of this tournament until you have a single winner. What type of a tree is this? If there are n contestants in a single elimination tournament, how many matches will be played? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.2.5 (Archived) | Use bin-packing techniques to solve problems concerning optimizing resource usage. Remarks: Example: Six large crates of electronic equipment are to be shipped to a warehouse. The crates weigh 2,800, 6,000, 5,400, 1,600, 6,800, and 5,000 pounds. Each delivery truck has a capacity of 10,000 pounds. What is the minimum number of trucks needed to send all the crates? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.3.1 (Archived) | Use election theory techniques to analyze election data. Remarks: Example: Each student in your class ranks four kinds of fruit drinks from the most preferred to least preferred. Discuss the merits of various methods for deciding on the overall ranking by the class. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.3.2 (Archived) | Use weighted voting techniques to decide voting power within a group. Remarks: Example: A company has 3 stockholders who have different numbers of votes according to their holdings as follows: 4, 3, and 2. The quota that is the number of votes needed to pass a motion is 5. Find the power index of each stockholder. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.3.3 (Archived) | Use fair division techniques to divide continuous objects. Remarks: Example: Find a method for dividing a piece of cake among three people so that each person feels they have received a fair share. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.3.4 (Archived) | Use fair division techniques to solve apportionment problems. Remarks: Example: Find the enrollment of seniors, juniors, sophomores, and freshmen at your high school. If there are 20 seats on the Student Council, how should the representatives be apportioned so that the voting power of each class is proportional to its size? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.4.1 (Archived) | Solve maximal profit/minimal cost problems. Remarks: Example 1: A country store sells GORP to hikers. The MountainClimber mix package contains one pound of peanuts mixed with four pounds of raisins and sells for $9.75. The Tenderfoot mix package contains two pounds of peanuts mixed with three pounds of raisins and sells for $9.50. The center has 60 pounds of peanuts and 120 pounds of raisins available. How many packages of each mix should the center sell to maximize its income? Example 2: A company produces two varieties of widgets —benchmark and deluxe. A benchmark widget takes 3 hours to assemble and 6 hours to finish. A deluxe widget takes 5 hours to assemble and 5 hours to finish. The assemblers can work no more than 45 hours per week and the finishers can work no more than 60 hours per week. The profit is $32 on a Benchmark widget and $40 on a deluxe widget. Find how many of each model should be produced each week to maximize profit. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.5.1 (Archived) | Use game theory to solve strictly determined games. Remarks: Example: Consider a card game where John gets a 4 of Hearts and a 5 of Clubs, and Susan gets a 3 of Clubs and a 6 of Hearts. The players each show one card simultaneously. The player who shows the card of larger value receives the sum of the numbers on the two cards shown. Set up the game matrix and find the optimal strategy and the value of the game. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.D.5.2 (Archived) | Use game theory to solve non-strictly determined games. Remarks: Example: In the game “Two-Finger Morra,” each of two players shows either one or two fingers. If the total number of fingers shown is even, Player A collects a dollar for each finger shown from Player B. If the total number of fingers is odd, Player A pays $3 to Player B. Set up the game matrix and find the optimal strategy and the value of the game. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.6.1 (Archived) | Use truth tables to determine truth values of propositional statements. Remarks: Students develop truth tables involving conjunctive, disjunctive, negation, conditional, and biconditional statements and use these truth tables to solve problems. Example 1: What is the truth value of the following statement? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.6.2 (Archived) | Find the converse, inverse, and contrapositive of a statement Remarks: Example: Determine the inverse, converse and contrapositive of the statement, “If it is Thursday, there will be rain.” Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.D.6.3 (Archived) | Determine whether two propositions are logically equivalent. Remarks: Example: Determine whether the propositions  and and  are logically equivalent. are logically equivalent.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.6.4 (Archived) | Use methods of direct and indirect proof and determine whether a short proof is logically valid. Remarks: Example: If somebody argues, “If it’s Thursday, it is raining.” along with “It is raining” implies that "it is Thursday.", is this a valid or invalid argument? Explain your answer. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.D.6.5 (Archived) | Identify and give examples of :
Remarks: Example 1: Do you prove axioms from theorems or theorems from axioms? Example 2: What type of reasoning are you using when you look for a pattern? Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.D.6.6 (Archived) | Construct logical arguments using laws of detachment (modus ponens), syllogism, tautology, and contradiction; judge the validity of arguments, and give counterexamples to disprove statements. Remarks: Example: Find an example to show that triangles with two sides and one angle equal are not necessarily congruent. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.D.6.7 (Archived) | Use applications of the universal and existential quantifiers to propositional statements. Remarks: Example: Use predicate logic formulas to write the following phrases: *Only dogs bark. *Everyone has a father. *If a number is an integer, then it is a rational number. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.7.1 (Archived) | Perform set operations such as union and intersection, complement, and cross product. Remarks: Example: Let A={1,2,3} and B={2,4,5} be two sets in universe U={1,2,3,4,5,6}. Find the union of A and B and the complement of B. Find AXB. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.D.7.2 (Archived) | Use Venn diagrams to explore relationships and patterns and to make arguments about relationships between sets.
Remarks: Example: Use a Venn diagram to give an argument that the intersection of A and B is a subset of the union of A and B. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.8.1 (Archived) | Use matrices to organize and store data. Perform matrix operations (addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, multiplication) Remarks: Example 1: Central High School offers three different styles of class rings — benchmark, classic, and deluxe. Each style is available in a girl’s ring and a boy’s ring. Make up your own data to show how many of each variety was sold and store the data in a matrix with rows and columns labeled. Example 2: For the following matrices perform the indicated operation, if possible: B-A , A+C, AC, CA, AB Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.D.8.2 (Archived) | Use matrix operations to solve problems. Remarks: Example: Suppose the rings in Example 1 for the benchmark MA.921.D.8.1 cost $90, $120, and $135 for the girls’ rings and $110, $140, and $165 for the boys’ rings. Display this information in a matrix and find the total revenue from the sale of girls’ rings and from the sale of boys’ rings. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.8.3 (Archived) | Use row-reduction techniques to solve problems. Remarks: Example: Solve this system of equations using an augmented matrix and row reduction: x - 2y + 3z = 5 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.8.4 (Archived) | Find the inverse of a matrix, and use the inverse to solve problems with and without the use of technology.
Remarks: Example: Solve the system of equations in Example 1 for the benchmark MA.912.D.8.3 using an inverse matrix. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.D.8.5 (Archived) | Use determinants of 2 x 2 and 3 x 3 matrices as well as higher order matrices with and without the use of technology. Remarks: Example 1: Explain why a square matrix is invertible if and only if its determinant is non-zero. Example 2: Use Cramer’s rule to solve a system of equations such as Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.D.8.6 (Archived) | Use matrices to solve Markov chain problems that link present events to future events using probabilities. Remarks: Example: Ms. Johnson has observed John’s grade in her Algebra II class for a long time. It seems that when John gets an A on a quiz, the probability he would get an A, B, C, D, F on the next quiz will be 5/10, 2/10, 2/10, 1/10, 0, respectively. When he gets B, the probability he would get an A, B, C, D, F on the next quiz will be 2/10, 5/10, 2/10, 1/10, 0, respectively. When he gets a C, the probability he would get an A, B, C, D, F on the next quiz will be 1/10, 2/10, 5/10, 1/10, 1/10, respectively. When he gets a D, the probability he would get an A, B, C, D, F on the next quiz will be 1/10, 1/10, 2/10, 5/10, 1/10, respectively. When he gets an F, the probability he would get an A, B, C, D, F on the next quiz will be 1/10, 1/10, 1/10, 2/10, 5/10, respectively. John got a B today on a quiz in Ms. Johnson’s class. What is the probability he would get an A after three quizzes? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.D.9.1 (Archived) | Demonstrate an understanding of the geometric interpretation of vectors and vector operations including addition, scalar multiplication, dot product, and cross product in the plane and in three-dimensional space.
Remarks: Example 1: Vectors u and v are shown below. Use these vectors to sketch 2u + 3v.  Example 2: Find the magnitude and direction of (3i+4j), where i is along x axis and j is along y axis. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.9.2 (Archived) | Demonstrate an understanding of the algebraic interpretation of vectors and vector operations including addition, scalar multiplication, dot product, and cross product in the plane and in three-dimensional space.
Remarks: Example: If u = ( 3, 1) and v = (-3, 2) , find the measure of the angle between vectors u and v. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.D.9.3 (Archived) | Use vectors to model and solve application problems. Remarks: Example: The vector 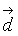 represents the displacement of a wagon that is pulled with the force represents the displacement of a wagon that is pulled with the force 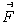 .The work done in moving the wagon in the direction of .The work done in moving the wagon in the direction of 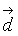 is defined to be the component of is defined to be the component of 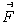 in the direction of in the direction of 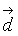 times the distance the wagon moves. Show that this definition can be written as , times the distance the wagon moves. Show that this definition can be written as , 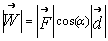 where α= the angle between where α= the angle between 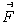 and and 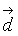 . And find the work done if . And find the work done if 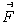 = (10,3) and = (10,3) and 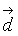 = (25,0). = (25,0).Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.F.1.1 (Archived) | Explain the difference between simple and compound interest. Remarks: Example: Compare the similarities and differences for calculating the final amount of money in your savings account based on simple interest or compound interest. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.F.1.2 (Archived) | Solve problems involving compound interest. Remarks: Example: Find the amount of money on deposit at the end of 5 years if you started with $500 and it was compounded quarterly at 6 % interest. Example: Joe won $25,000 in the lottery. How many years will it take at 6% interest compounded yearly for his money to double? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.F.1.3 (Archived) | Demonstrate the relationship between simple interest and linear growth.
Remarks: Example: Find the account balance at the end of each month for a 5 month span for $1500 @ 3 % interest based on simple interest for 1 year. Graph this scenario and explain if this is a linear or exponential problem. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.F.1.4 (Archived) | Demonstrate the relationship between compound interest and exponential growth.
Remarks: Example: Using an exponential function, find the account balance at the end of 4 years if you deposited $1300 in an account paying 3.5% interest compounded annually. Graph the scenario. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.F.2.1 (Archived) | Calculate the future value of a given amount of money with and without technology.
Remarks: Example: Suppose you have $750 on January 1, 2007. If you deposit this in an account paying 5% interest, compounded quarterly, how much money will be in the account on January 1, 2012? Example: Suppose you deposit $400 into an account at the beginning of each year, starting Jan 1, 2007. If the account pays 6% interest, compounded annually, how much will be in the account at the end of 5 years? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.F.2.2 (Archived) | Calculate the present value of a certain amount of money for a given length of time in the future with and without technology.
Remarks: Example: A five year, zero-coupon bond pays 5% annual interest, and has a face value of $1,000. If the bond matures on Dec 31, 2010, what was the original purchase price of the bond? Example: Find the present value of an annuity paying $500 per year for 10 years at 6% annual interest. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.2.3 (Archived) | Use a consumer price index to express dollars in constant terms with and without technology.
Remarks: Example: The U.S. Consumer Price Index for January 2000 was 168.8, and in January 2006 was 198.3. If a worker was making a monthly salary of $2500 in January 2000, how much would (s)he need to earn in January 2006 to keep pace with inflation? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.2.4 (Archived) | Calculate the present value of an income stream with and without technology.
Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.F.3.1 (Archived) | Compare the advantages and disadvantages of using cash versus a credit card. Remarks: Example: Compare paying for a tank of gasoline in cash or paying with a credit card over a period of time. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.F.3.2 (Archived) | Analyze credit scores and reports. Remarks: Example: Explain how each of the following categories affects a credit score: 1) past payment history, 2) amount of debt, 3) public records information, 4) length of credit history, and 5) the number of recent credit inquiries. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.3 (Archived) | Calculate the finance charges and total amount due on a credit card bill. Remarks: Example: Calculate the finance charge each month and the total amount paid for 5 months if you charged $500 on your credit card but you can only afford to pay $100 each month. Your credit card has a monthly periodic finance rate of .688% and an annual finance rate of 8.9%. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.F.3.4 (Archived) | Compare the advantages and disadvantages of deferred payments. Remarks: Example: Compare paying on a college loan between a Stafford loan or a PLUS loan two years after graduation Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.F.3.5 (Archived) | Calculate deferred payments. Remarks: Example: You want to buy a sofa that cost $899. Company A will let you pay $100 down and then pay the remaining amount over 3 years at 22% interest. Company B will not make you pay a down payment and they will defer payments for one year. However, you will accrue interest at a rate of 20 % interest during that first year. Starting the second year you will have to pay the new amount for 2 years at a rate of 26 % interest. Which deal is better and why? Calculate the total amount paid for both deals. Example: An electronics company advertises that you don't have to pay anything for 2 years. If you bought a big screen TV for $2999 on January 1st what would your balance be two years later if you haven't made any payments assuming an interest rate of 23.99%? What would your monthly payments be to pay the TV off in 2 years? What did the TV really cost you? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.6 (Archived) | Calculate total cost of purchasing consumer durables over time given different down payments, financing options, and fees. Remarks: Example: Find the actual cost of a car and interest charged with a showroom price of $15,999, down payment of $1,600, rate of interest of 12%, and 30 monthly payments. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.F.3.7 (Archived) | Calculate the following fees associated with a mortgage:
Remarks: Example: 1) Calculate the total amount of fees on a $230,000 mortgage if the lender: charges 2 points and a 0.5% origination fee. 2) Calculate the maximum brokerage fee on a net loan of $184,000, 3) A seller has agreed to pay the Documentary Stamps on a property worth $150,000 (selling price). The purchaser is responsible for the Documentary Stamps on the $75,000 mortgage being assumed and the new $25,000 second mortgage. Calculate all applicable amounts. 4) A $185,340 loan carries at a 5.625% annual interest rate. Using the 365 day method, how much interest would a buyer owe for the 22 days remaining for a May closing. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.F.3.8 (Archived) | Substitute to solve a variety of mortgage formulas, including but not limited to Front End Ratio, Total Debt-to-Income Ratio, Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV), Combined Loan-to-Value Ratio (CLTV), and Amount of Interest Paid Over the Life of a Loan. Remarks: Example: Mr. Lindsey purchased a home for $129,000. It was appraised at $95,000. He was assuming a $52,000 first mortgage, and he obtained a 2nd mortgage for the lenders maximum CLTV of 90%. What would be the amount of the down payment? Example: Calculate the interest scheduled to be paid over the life of a $190,000 mortgage loan with a term of 30 years and fixed monthly payment of $1250.50. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.F.3.9 (Archived) | Calculate the total amount to be paid over the life of a fixed rate loan. Remarks: Example: Calculate the total amount to be paid for a $275,000 loan at 5.75% interest over 30 years Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.10 (Archived) | Calculate the effects on the monthly payment in the change of interest rate based on an adjustable rate mortgage. Remarks: Example: You would like to borrow $245,000 using a 30-year, 1-year ARM indexed to the 1-year Treasury security with a 2.75 percent margin and 2/6 caps (2 percent per year and 6 percent lifetime). The initial interest rate on this loan is 2.75 percent. The lender is charging you 1.50 points and $1,200 in miscellaneous fees to close the loan. a) What is the initial payment on this mortgage? b) If the 1- year Treasury security is yielding 2.25 percent at the first adjustment date, what is your payment on this loan during the second year? c) Suppose that the 1-year Treasury is yielding 2.75 percent at the second adjustment date. What is the new payment on this loan during the third year? d) Assuming that you pay of the loan at the end of the third year, what yield did the lender earn on this loan? Now resolve all four parts of the last problem assuming that the loan has a 20 percent payment cap instead of 2/6 interest rate caps. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.11 (Archived) | Calculate the final pay out amount for a balloon mortgage. Remarks: Example: If you have a 5-year balloon mortgage with a 15 year amortization schedule, a rate of 6.5%, and a $100,000 loan what would the remaining balance be after the end of the fifth year? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.12 (Archived) | Compare the cost of paying a higher interest rate and lower points versus a lower interest rate and more points. Remarks: Example: Assuming all of the following were originally 15 year mortgages, which fixed rate mortgage cost the mortgagor the least? a) 7.375% interest + 0 points paid off in 10 years b) 7.375% interest + 0 points paid off in 7 years c) 7 % interest + 3 points paid off in 10 years d) 7 % interest + 3 points paid off in 7 years Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.13 (Archived) | Calculate the total amount paid for the life of a loan for a house including the down payment, points, fees, and interest. Remarks: Example: Calculate the total amount paid for a $100,000 house with a 15 year fixed rate loan at 5.65% if the mortgagor pays a $25,000 down payment; 2 points; 1% origination fee; maximum brokerage fee on a net loan; and State Documentary Stamps on the deed at a tax rate of $.70 per $100, the mortgage note at a tax rate of $.35 per $100, a and Intangible Tax at a rate of .002. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.14 (Archived) | Compare the total cost for a set purchase price using a fixed rate, adjustable rate, and a balloon mortgage. Remarks: Example: Find the total cost for a $225,000 mortgage for the following options: a) 30 year fixed rate mortgage with a rate of 6.35 % b) 3/1 ARM with a rate of 6.75% with a maximum adjustment of 2 points per year with a cap of 6 points for 30 years c) 10 year balloon mortgage with a 30 year amortization schedule with a rate of 5.5% Next describe the benefits and detriments of each mortgage option. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.15 (Archived) | Interpret the legal description using the metes and bounds; lot and block (plat); government survey; and monument methods. Remarks: Example: Given an unmarked parcel of land and an accurate point of beginning POB) draw in the boundary lines using the given angles and distances. Example: Find a specific lot on a plot. Example: Find a specific range on a government survey. Example: Write a legal description for a specific piece of property using natural topographical features (monument method). Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.16 (Archived) | Estimate real property value using the sales comparison approach, cost-depreciation approach, or the income capitalization approach. Remarks: Example: Use the cost-depreciation approach to estimate the real property value of a given home at current builders' market cost per square foot. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.3.17 (Archived) | Compare interest rate calculations and annual percentage rate calculations to distinguish between the two rates. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.F.4.1 (Archived) | Develop personal budgets that fit within various income brackets. Remarks: Example: Develop a budget worksheet that includes typical expenses such as housing, transportation, utilities, food, medical expenses, and miscellaneous expenses. Add categories for savings toward your own financial goals, and determine the monthly income needed, before taxes, to meet the requirements of your budget. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.F.4.2 (Archived) | Explain cash management strategies including debit accounts, checking accounts, and savings accounts. Remarks: Example: Explain the difference between a checking account and a savings account. Why might you want to have both types of accounts? Why might you want to have only one or the other type? Why is it rare to find someone who has a savings account but no checking account? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.F.4.3 (Archived) | Calculate net worth. Remarks: Example: Jose is trying to prepare a balance sheet for the end of the year. His balances and details for the year are given in the table below. Write a balance sheet of Jose's liabilities and assets, and compute his net worth. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.F.4.4 (Archived) | Establish a plan to pay off debt.
Remarks: Example: Suppose you currently have a balance of $4500 on a credit card that charges 18% annual interest. What monthly payment would you have to make in order to pay off the card in 3 years, assuming you do not make any more charges to the card? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.F.4.5 (Archived) | Develop and apply a variety of strategies to use tax tables, and to determine, calculate, and complete yearly federal income tax.
Remarks: Example: Suppose that Joe had income of $40,000 in 2005, and had various deductions totaling $6,240. If Joe filed as a single person, how much income tax did he have to pay that year? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.F.4.6 (Archived) | Compare different insurance options and fees. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.F.4.7 (Archived) | Compare and contrast the role of insurance as a device to mitigate risk and calculate expenses of various options.
Remarks: Example: Explain why a person might choose to buy life insurance. Are there any circumstances under which one might not want life insurance? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.4.8 (Archived) | Collect, organize, and interpret data to determine an effective retirement savings plan to meet personal financial goals. Remarks: Example: Investigate historical rates of return for stocks, bonds, savings accounts, mutual funds, as well as the relative risks for each type of investment. Organize your results in a table showing the relative returns and risks of each type of investment over short and long terms, and use these data to determine a combination of investments suitable for building a retirement account sufficient to meet anticipated financial needs. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.4.9 (Archived) | Calculate, compare, and contrast different types of retirement plans, including IRAs, ROTH accounts, and annuities. Remarks: Example: Suppose you put $5000 per year into an IRA for 40 years. If the account pays 6% per year interest, how much would you have at the end of the 40 years? If, at that time, you are in the 15% income tax bracket, how much would this be after taxes? Suppose that, instead, you paid the tax each year on the $5000 at your current rate of 28% and put the remaining funds in a ROTH account paying 6% interest. How much would you then have after 40 years? Which appears to be the better option? What are some of the risks of deferring tax payments until retirement? Example: Explain the difference between an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) and a ROTH account. Why might somebody choose to put retirement funds in a ROTH account rather than an IRA? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.F.4.10 (Archived) | Analyze diversification in investments. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.F.4.11 (Archived) | Purchase stock with a set amount of money, and follow the process through gains, losses, and selling.
Remarks: Example: At the beginning of the year, Mary invests $3000, buying $1500 of Stock A at $30 per share, $1000 of Stock B at $40 per share, and putting $500 in a money market account paying 5% interest. At the end of the year, stock A is priced at $34 per share, and stock B is priced at $38 per share. What is the overall rate of return for the year on Mary's investments? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.4.12 (Archived) | Compare and contrast income from purchase of common stock, preferred stock, and bonds. Remarks: Example: Explain the difference between common and preferred stock. What are some reasons people might choose common stock over preferred stock? Which type of stock is more prevalent in the market today? Example: Compare corporate bonds, government bonds, and common stock as investments with respect to the following attributes: rates of return, price risk, default risk, and taxability of earnings Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.F.4.13 (Archived) | Given current exchange rates be able to convert from one form of currency to another. Remarks: Example: Suppose you are traveling in Europe, and while there you withdraw 150 Euros to pay for expenses. If the exchange rate at the time was $1.27 per Euro, how much money (in dollars) was charged to your bank account? Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.F.4.14 (Archived) | Use data to compare historical rates of return on investments with investment claims to make informed decisions and identify potential fraud. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.F.5.1 (Archived) | Demonstrate how price and quantity demanded relate, how price and quantity supplied relate, and how price changes or price controls affect distribution and allocation in the economy. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.F.5.2 (Archived) | Use basic terms and indicators associated with levels of economic performance and the state of the economy. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.G.1.1 (Archived) | Find the lengths and midpoints of line segments in two-dimensional coordinate systems. Remarks: Example: Find the length and midpoint of the line segment joining the points A (3, -8) and B (9, 0). Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.1.2 (Archived) | Construct congruent segments and angles, angle bisectors, and parallel and perpendicular lines using a straight edge and compass or a drawing program, explaining and justifying the process used. Remarks: Example 1: Draw a triangle ABC. Duplicate it using your compass and straightedge. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.G.1.3 (Archived) | Identify and use the relationships between special pairs of angles formed by parallel lines and transversals. Remarks: Example: In the diagram, the lines k and l are parallel. Find the value of x. Find all angle values in the diagram. Explain your answer.  Example 2: In the diagram, the lines m and n are parallel. Find the value of x. Explain your answer. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.1.4 (Archived) | Use coordinate geometry to find slopes, parallel lines, perpendicular lines, and equations of lines. Remarks: Example 1: Given points P(2,-1), Q(-4, 2), and M(5,3), find the coordinates of a point N such that  and and 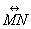 are parallel. Find coordinates of a point K such that are parallel. Find coordinates of a point K such that 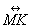 is perpendicular to is perpendicular to 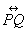 . . Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.G.2.1 (Archived) | Identify and describe convex, concave, regular, and irregular polygons. Remarks: Example 1: Draw a hexagon. Is it convex or concave? Is it regular or irregular? Explain your answers. Example 2: Define the terms convex, concave, regular and irregular polygon and draw a picture of the tern next to the definition. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.2.2 (Archived) | Determine the measures of interior and exterior angles of polygons, justifying the method used. Remarks: Example 1: Calculate the measure of one interior angle and one exterior of a regular octagon. Explain your method. Example 2: Suppose that you will make a picture frame like the one shown below. To make the regular hexagonal frame, you will use identical trapezoidal pieces. What are the measures of the angles of the trapezoids? Explain your answer.  Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.2.3 (Archived) | Use properties of congruent and similar polygons to solve mathematical or real-world problems. Remarks: Example: Suppose a building is in the shape of a regular hexagon. The architect wants to put walkways as indicated. Show that the triangles formed are equal in size and shape. 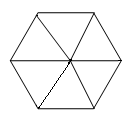 Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.2.4 (Archived) | Apply transformations (translations, reflections, rotations, dilations, and scale factors) to polygons. to determine congruence, similarity, and symmetry. Know that images formed by translations, reflections, and rotations are congruent to the original shape. Create and verify tessellations of the plane using polygons. Remarks: Physical objects, drawings, and dynamic geometry software might help students explore this benchmark. Students' early work in elementary and middle school should form a base for teaching this benchmark (see MA.3.G.3.3, MA.4.G.5.2, and MA.7.G.4.2). Students should explore different types of transformations and observe that some transformations (translations, reflections, and rotations) result in congruent shapes. Example: Explore regular polygons through manipulatives and/or drawing programs. Describe which of the polygons would be best for tiling a rectangular floor. Explain your reasoning. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.2.5 (Archived) | Explain the derivation and apply formulas for perimeter and area of polygons (triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, etc.). Remarks: Example 1: A rectangle of area 360 square yards is ten times as long as it is wide. Find its length and width. Example 2: Explain the derivation of the formula for the area of a triangle. Example 3: The design below is called the Ohio Star. Assuming that it measures 9 inches by 9 inches, calculate the total area of all the orange patches, the total area of all the yellow patches, and the total area of all the green patches. How much fabric of each color will you need to cover an area that measures 72 inches by 90 inches?  Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.2.6 (Archived) | Use coordinate geometry to prove properties of congruent, regular and similar polygons, and to perform transformations in the plane. Remarks: Example: Draw the polygon defined by the following vertices ( 1, 3), ( -1, 3), (3, 1), (-3, 1), (1, -3), (-1, -3), (-3, -1), (3, -1). Is this polygon regular? Justify your answer. Example: Is the polygon formed by connecting the points (2, 1), ( 6, 2), (5, 6), and (1, 5) a square? Justify your answer. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.2.7 (Archived) | Determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter and area of common geometric figures. Remarks: Example: If the lengths of each side of a trapezoid are tripled, determine the change in its area, and justify your answer. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.G.3.1 (Archived) | Describe, classify, and compare relationships among quadrilaterals including the square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezoid, and kite. Remarks: This benchmark examines properties of quadrilaterals one at a time. Example: Explore a trapezoid through manipulatives, drawings and/or technology. Draw the diagonals and determine whether they are perpendicular. Give a convincing argument that your judgment is correct. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.3.2 (Archived) | Compare and contrast special quadrilaterals on the basis of their properties. Remarks: This benchmark examines similarities and differences between different types of quadrilaterals. Example: Explain the similarities and differences between a rectangle, rhombus, and kite. Create a Venn diagram to match your explanation. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.3.3 (Archived) | Use coordinate geometry to prove properties of congruent, regular, and similar quadrilaterals. Remarks: Coordinate geometry is used while students prove quadrilaterals to be congruent, similar, or regular. Coordinate geometry is used to prove properties of quadrilaterals. Example: Given a quadrilateral with vertices (0, 0), (5/2, 5sqrt(3)/2), (5, 0), (7, 7sqrt(3)/3), prove that the diagonals of this quadrilateral are perpendicular. Example: Is rectangle ABCD with vertices at A(0, 0), B(4, 0), C(4, 2), D(0, 2) congruent to rectangle PQRS with vertices at P(-2, -1), Q(2, -1), R(2, 1), S(-2, 1)? Justify your answer. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.3.4 (Archived) | Prove theorems involving quadrilaterals. Remarks: Example: Prove that the diagonals of a rectangle are congruent. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.G.4.1 (Archived) | Classify, construct, and describe triangles that are right, acute, obtuse, scalene, isosceles, equilateral, and equiangular. Remarks: Students may use a compass and straightedge or a drawing program to construct and classify triangles, and describe the attributes of each triangle. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.4.2 (Archived) | Define, identify, and construct altitudes, medians, angle bisectors, perpendicular bisectors,orthocenter, centroid, incenter, and circumcenter. Remarks: Example: Draw several triangles. Construct their angle bisectors. What do you observe from your drawings? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.4.3 (Archived) | Construct triangles congruent to given triangles. Remarks: Example: Given a triangle, construct a congruent triangle and prove that the two triangles are congruent. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.G.4.4 (Archived) | Use properties of congruent and similar triangles to solve problems involving lengths and areas. Remarks: Example: Of two similar triangles, the second has sides half the length of the first. The area of the first triangle is 20 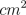 . what is the area of the second triangle? . what is the area of the second triangle?Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.4.5 (Archived) | Apply theorems involving segments divided proportionally. Remarks: Example: In triangle ABC shown below, 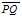 is parallel to is parallel to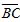 . What is the length of . What is the length of 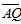 ? ?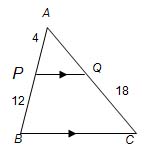 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.4.6 (Archived) | Prove that triangles are congruent or similar and use the concept of corresponding parts of congruent triangles. Remarks: Example: Prove that triangles ABC and APQ are similar. 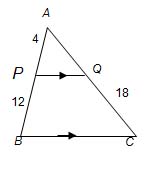 Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.4.7 (Archived) | Apply the inequality theorems: triangle inequality, inequality in one triangle, and the Hinge Theorem. Remarks: Example: Can you draw a triangle with sides of length 7 cm, 4 cm, and 15 cm? Explain your answer. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.4.8 (Archived) | Use coordinate geometry to prove properties of congruent, regular, and similar triangles. Remarks: Example: Draw a triangle with vertices at (1, 3), (2, 5), and (6, 1). Draw another triangle with vertices at (-3, -1), (-2, 1), and (2, -3). Are these triangles congruent, similar or neither? Defend your answer. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.G.5.1 (Archived) | Prove and apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. Remarks: Example: Determine if the triangle with side lengths of 10, 12, and 18 is a right triangle. Justify your reasoning. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.5.2 (Archived) | State and apply the relationships that exist when the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle. Remarks: Example: Find the value of x in the right triangle below. 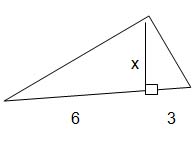 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.G.5.3 (Archived) | Use special right triangles (30° - 60° - 90° and 45° - 45° - 90°) to solve problems. Remarks: Example: An isosceles right triangle has one leg 6 cm long. Find the lengths of the other two sides. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.5.4 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems involving right triangles. Remarks: Example: The distance of the base of a ladder from the wall it leans against should be at least 1/3 of the ladder's total length. Suppose a 12-ft ladder is placed according to these guidelines. Give the minimum distance of the base of the ladder from the wall. How far up the wall will the ladder reach? Explain and include a sketch in your explanation. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.G.6.1 (Archived) | Determine the center of a given circle. Given three points not on a line, construct the circle that passes through them. Construct tangents to circles. Circumscribe and inscribe circles about and within triangles and regular polygons. Remarks: Example: Given a circle, find its center by drawing the perpendicular bisectors of two chords. Example: Given a circle and a point on the circle, construct a tangent to the circle, passing through the given point. Example: Draw an acute triangle and construct the circumscribed circle. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.G.6.2 (Archived) | Define and identify: circumference, radius, diameter, arc, arc length, chord, secant, tangent and concentric circles. Remarks: Example: What is the angle between a tangent to a circle and the radius at the point where the tangent meets the circle? Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.G.6.3 (Archived) | Prove theorems related to circles, including related angles, chords, tangents, and secants. Remarks: Example: Prove that a segment from the center of a circle perpendicular to a chord, bisects the chord. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.G.6.4 (Archived) | Determine and use measures of arcs and related angles (central, inscribed, and intersections of secants and tangents). Remarks: Example: Find the measure of angle ABC in the diagram below. 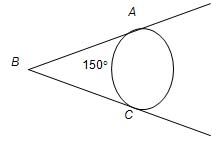 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.6.5 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems using measures of circumference, arc length, and areas of circles and sectors. Remarks: Example: Which will give you more: three 6-inch pizzas or two 8-inch pizzas? Explain your answer. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.6.6 (Archived) | Given the center and the radius, find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane or given the equation of a circle in center-radius form, state the center and the radius of the circle. Remarks: Example: Find the equation of the circle with radius 10 and center (6, -3). Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.6.7 (Archived) | Given the equation of a circle in center-radius form or given the center and the radius of a circle, sketch the graph of the circle. Remarks: Example: Sketch the graph of the circle whose equation is 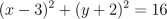 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.G.7.1 (Archived) | Describe and make regular, non-regular, and oblique polyhedra, and sketch the net for a given polyhedron and vice versa. Remarks: Example: Make a net for a tetrahedron out of poster board and fold it up to make the tetrahedron. Is this a regular polyhedron? Explain why or why not. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.7.2 (Archived) | Describe the relationships between the faces, edges, and vertices of polyhedra. Remarks: Example: Use manipulatives to investigate the relationships between faces, edges, and vertices of polyhedra; i.e., Euler's Theorem. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.G.7.3 (Archived) | Identify, sketch, find areas and/or perimeters of cross sections of solid objects. Remarks: Example: What cross sections can you get from each of these figures? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.G.7.4 (Archived) | Identify chords, tangents, radii, and great circles of spheres Remarks: Example: On Earth, is the equator a great circle? Explain your answer. 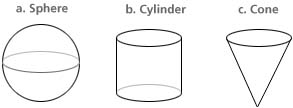 Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall
|
| MA.912.G.7.5 (Archived) | Explain and use formulas for lateral area, surface area, and volume of solids. Remarks: Example: A gold class ring is dropped into a glass that is a right cylinder with a 6 cm diameter. The water level rises 1 mm. What is the volume of the ring? Example: Given the composite solid consisting of a hemisphere and a cone, calculate the surface area and the volume. 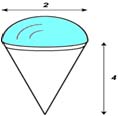 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.7.6 (Archived) | Identify and use properties of congruent and similar solids. Remarks: Example: Explain how the surface area and volume of similar cylinders are related Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.7.7 (Archived) | Determine how changes in dimensions affect the surface area and volume of common geometric solids. Remarks: Example: Explain how changing the radius or height of a cylinder affects its surface area and volume. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.G.8.1 (Archived) | Analyze the structure of Euclidean geometry as an axiomatic system. Distinguish between undefined terms, definitions, postulates, and theorems. Remarks: Example: Classify each of the following as an undefined term, defined term, postulate, or theorem:
Students should also explore non-Euclidean geometries including hyperbolic and elliptic geometries. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.G.8.2 (Archived) | Use a variety of problem-solving strategies, such as drawing a diagram, making a chart, guess-and-check, solving a simpler problem, writing an equation, and working backwards. Remarks: Example: How far does the tip of the minute hand of a clock move in 20 minutes if the tip is 4 inches from the center of the clock? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.G.8.3 (Archived) | Determine whether a solution is reasonable in the context of the original situation. Remarks: Example: The area of a circle is 49p and George determined that the diameter is 7. Is his answer reasonable? Why or why not? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.G.8.4 (Archived) | Make conjectures with justifications about geometric ideas. Distinguish between information that supports a conjecture and the proof of a conjecture. Remarks: Example: Calculate the ratios of side lengths in several different-sized triangles with angles of 90°, 50°, and 40°. What do you notice about the ratios? How might you prove that your observation is true (or show that it is false)? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.G.8.5 (Archived) | Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction and proofs involving coordinate geometry. Use and compare a variety of ways to present deductive proofs, such as flow charts, paragraphs, two-column, and indirect proofs. Remarks: Example: Prove that the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. Example: Prove that the perpendicular bisector of line segment AB is the set of all points equidistant from the endpoints A and B. Example: Prove that two lines are parallel if and only if the alternate interior angles the lines make with a transversal are equal. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.G.8.6 (Archived) | Perform basic constructions using straightedge and compass, and/or drawing programs describing and justifying the procedures used. Distinguish between sketching, constructing, and drawing geometric figures.
Remarks: Example: Construct a line parallel to a given line through a given point not on the line, explaining and justifying each step. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.P.1.1 (Archived) | Use counting principles, including the addition and the multiplication principles, to determine size of finite sample spaces and probabilities of events in those spaces. Remarks: Example: A dinner menu has three choices for appetizers, five choices for main dishes, and four options for dessert. How many different choices of one appetizer, one main dish, and one dessert are there? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.P.1.2 (Archived) | Use formulas for permutations and combinations to count outcomes and determine probabilities of events. Remarks: Example: You are one of 15 potential members of a committee. A committee of 4 people will be chosen at random from the 15. How many possible committees can be formed? If 6 of the potential members are women, what is the probability of all the committee members being women? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.P.2.1 (Archived) | Determine probabilities of complementary events, and calculate odds for and against the occurrence of events. Remarks: Example: Suppose Antonio makes 75% of his foul shots in basketball. If he gets to attempt two shots, what is the probability of his making at least one of the two shots? What are the odds against missing both shots? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.P.2.2 (Archived) | Determine probabilities of independent events. Remarks: Example: A fair coin is tossed four times. What is the probability of getting heads on at least two of the tosses? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.P.2.3 (Archived) | Understand and use the concept of conditional probability, including: understanding how conditioning affects the probability of events and finding conditional probabilities from a two-way frequency table.
Remarks: Example: In a certain large city, 25% of all wage earners have a college degree. Of those who do have a college degree, 10% earn more than $80,000 per year, and of those who do not, 4% earn more than $80,000 per year. If a randomly selected wage earner earns more than $80,000 per year, what is the probability that (s)he has a college degree? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.P.3.1 (Archived) | Determine probabilities of events from distributions, including:
Remarks: Example: Suppose that 60% of the general population are basketball fans. If 8 people are chosen at random, what is the probability that 4 of them will be basketball fans? Example: Math SAT scores are normally distributed with mean 500, standard deviation 100. What is the probability that Joan's SAT score is greater than 550? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.P.3.2 (Archived) | Determine the mean and variance of distributions, including:
Remarks: Example: A fair coin is flipped 10 times. Find the mean and variance of the number of heads. Example: continuous distribution Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.P.3.3 (Archived) | Apply the properties of the normal distribution. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.P.3.4 (Archived) | Apply the Central Limit Theorem to determine the probability that a sample mean will be in a certain interval. Remarks: Example: During a certain week the mean price of gasoline in Florida was $2.164 per gallon. What is the probability that the mean price for a sample of 38 gas stations in Florida is between $2.169 and $2.179? Assume the population standard deviation = $0.049. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.S.1.1 (Archived) | Formulate an appropriate research question to be answered by collecting data or performing an experiment. Remarks: Example: An article in the local paper states that the health of Americans has declined over the past decade. How can this assertion be stated in a way that allows for scientific testing? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.1.2 (Archived) | Determine appropriate and consistent standards of measurement for the data to be collected in a survey or experiment. Remarks: Example: A student is designing a survey to gauge levels of stress in a population of high schools students. Is "stress" something that can be directly measured? How should the student define "stress" so that it can be objectively and consistently measured? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.S.2.1 (Archived) | Compare the difference between surveys, experiments, and observational studies and what types of questions can and cannot be answered by a particular design.
Remarks: Example: Which kind of statistical study should be used (and why) to study each of the following: a) What percent of the voting age population in Florida favors making English the official language? b) What wavelength of light is best for plant growth? c) What is the relationship between x-ray exposure and cancer rates? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.2.2 (Archived) | Apply the definition of random sample and basic types of sampling, including representative samples, stratified samples, censuses. Remarks: Example: A survey is being planned to determine public opinion on a pending proposal to reform Social Security, and specifically whether there are differences by age group, political affiliation, and educational level. Choose and justify the appropriate type of sample to use? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.S.2.3 (Archived) | Identify sources of bias, including sampling and nonsampling errors. Remarks: Example: An Internet poll is conducted to determine the average educational level of adults in Florida. Describe possible sources of bias in the results of the poll. How useful are the results? Example: A survey asks a sample of students questions about their drug use. What sources of bias might enter into the results? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.S.3.1 (Archived) | Read and interpret data presented in various formats. Determine whether data is presented in appropriate format, and identify possible corrections. Formats to include:
Remarks: Example: The chart below shows the average daily high and low temperatures in an Australian city. What is the average high temperature in January? What is the average low temperature in March? Which month has higher temperatures, January or April? Can you think of a reason for this? Example: Compare the distributions of pulse rates for males and females by interpreting the following box and whisker plots:   Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.S.3.2 (Archived) | Collect, organize, and analyze data sets, determine the best format for the data and present visual summaries from the following:
Remarks: Example: Gather data to answer the question: which area of the country has the highest dropout rate? Display your dropout data in appropriate formats. Example: given a set of data, use appropriate technology to sort the data and to display a histogram or other chart. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.S.3.3 (Archived) | Calculate and interpret measures of the center of a set of data, including mean, median, and weighted mean, and use these measures to make comparisons among sets of data. Remarks: Example: A sample of five runs for bus A had passenger loads of 15, 24, 19, 12, and 20 passengers. A similar sample for bus B had passenger loads of 18, 21, 16, 14, and 16 passengers. Based on these samples, calculate the mean and median for the number of passengers for each bus. Which bus carries larger passenger loads? How does the answer to that question depend on which measure is being used (mean verses median)? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.S.3.4 (Archived) | Calculate and interpret measures of variance and standard deviation. Use these measures to make comparisons among sets of data. Remarks: Example: Monthly average high temperatures for Orlando are: 72, 73, 77, 83, 88, 91, 92, 92, 89, 84, 77, 73, while monthly average high temperatures for Tallahassee are: 64, 67, 73, 80, 87, 90, 91, 91, 88, 81, 72, 65. Which city has the greater variation in average high temperatures? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.S.3.5 (Archived) | Calculate and interpret the range and quartiles of a set of data. Remarks: Example: Scores on a recent math test in a certain class were as follows: 77, 84, 91, 50, 75, 95, 62, 83, 85, 78, 68, 92, 74, 81, 92, 98, 83, 73, 100, 71. Find the range of the test scores, and compute the interquartile range (IQR). Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.S.3.6 (Archived) | Use empirical rules such as the 68-95-99.7 rule to estimate spread of distributions and to make comparisons among sets of data.
Remarks: Example: The weights, in grams, of 16 randomly selected mice are: 15.7, 13.1, 13.9, 13.4, 14.8, 16.9, 14.2, 14.7, 13.7, 15.8, 16.7, 15.6, 16.1, 16.3, 14.1, 17.0. Find the variance of this set of data, and use the empirical rule to estimate the range of weights of the entire population of mice. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.S.3.7 (Archived) | Calculate the correlation coefficient of a set of paired data, and interpret the coefficient as a measure of the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.S.3.8 (Archived) | Determine whether a data distribution is symmetric or skewed based on an appropriate graphical presentation of the data. Remarks: Example: The graph below shows the probability density function of a continuous distribution. Determine whether the distribution is skewed left, skewed right, or symmetric.  Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.S.3.9 (Archived) | Identify outliers in a set of data based on an appropriate graphical presentation of the data, and describe the effect of outliers on the mean, median, and range of the data. Remarks: Example: The dotplot for the number of hours worked by 50 employees in one week at a firm is shown below. Are there any points that appear to be outliers?  Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.S.4.1 (Archived) | Explain and interpret the concepts of confidence level and "margin of error."
Remarks: Example: A newspaper article states that a recent poll on a topic has a margin of error of plus or minus 4%. Explain what this means in terms of the distribution of the actual population. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.4.2 (Archived) | Use a simulation to approximate sampling distributions for the mean, using repeated sampling simulations from a given population. Remarks: Example: The histogram below shows the distribution of the sample mean when samples of 15 random digits are selected (with replacement) and the sample mean is computed, with the process repeated 100 times to generate 100 sample means. What type of distribution does this resemble? If you visually estimate the mean from the histogram, how does it compare with the mean of the original uniform distribution?
Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.4.3 (Archived) | Apply the Central Limit Theorem to solve problems. Remarks: Example: Suppose you plotted a histogram of 100 sample means from a certain distribution. Would the histogram be more symmetrical if you used samples of size 10 or of size 20? Which sample size would result in a more widely spread out histogram? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.4.4 (Archived) | Approximate confidence intervals for means using simulations of the distribution of the sample mean. Remarks: Example: In an observational study, the waiting times for service of 10 randomly chosen customers in one day at a fast food restaurant are recorded, and the mean of the sample noted. This process is repeated for 50 days, with the resulting histogram of the sample means shown below. Use this histogram to estimate a 90% confidence interval for the mean wait time at this restaurant.  Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.4.5 (Archived) | Find the equation of the least squares regression line for a set of data. Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.S.5.1 (Archived) | Analyze the relationship between confidence level, margin of error, and sample size.
Remarks: Example: A pollster wishes to estimate the proportion of United States voters who favor capital punishment. How large a sample is needed in order to be 95% confident that the sample proportion will not differ from the true proportion by more than 2%? Example: Compared to a margin of error based on 95% confidence and a sample size of n=36, explain how margin of error changes when A) 99% confidence is used. B) A sample size of n=30 is used. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.5.2 (Archived) | Apply the general principles of hypothesis testing. Remarks: Example: Can you use a hypothesis test to prove that the average height of an adult male is 6 feet? Why or why not? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.5.3 (Archived) | Explain and identify the following: null hypothesis, alternative hypotheses, Type I error, and Type II error. Remarks: Example: According to the norms established for a history test, eighth graders should average 81.7 with a standard deviation of 8.5. a. Identify null and alternative hypotheses to be used for an experiment to test students' performance on the test. b. Explain what a Type I and a Type II error would be in the context of the null and alternative hypotheses given in (a). Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.5.4 (Archived) | Explain the meaning of p-value and its role in hypothesis testing. Remarks: Example: A statistical analysis of an experiment yields a p-value of 0.02. Explain the meaning of this p-value in terms of the decision that is made about the null and alternative hypotheses and Type I error. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.S.5.5 (Archived) | Perform hypothesis tests of means and proportions for large samples, using simulations to determine whether a sample mean (proportion) has a low likelihood of occurring. Remarks: Example: A student wants to determine whether a certain coin is fair. She flips it 20 times, and notes that it came up heads 65% of the time (13 times out of 20). A computer simulation of the same experiment with a fair coin, repeated 100 times, yielded varying results, shown in the histogram below. How many of the 100 experiments done by the computer resulted in 65% or more heads?  Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.5.6 (Archived) | Interpret the results of hypothesis tests of means and proportions, and make decisions based on p-values of test. Remarks: Example: In an effort to determine whether a school's ACT scores are going up, the school looked at a sample of scores from 10 current seniors, and found the sample mean to be 27.5. Historically, scores have been normally distributed with a mean of 25 and standard deviation of 4. If the school adopts a null hypothesis that the mean is still 25, and a one-sided alternative, the sample mean yields a p-value of 0.023. Determine whether this is good evidence that ACT scores have gone up, and write a summary explanation of your decision suitable for a presentation to a non-statistics-minded audience. If the alternative hypothesis were two-sided, what would the p-value be? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.5.7 (Archived) | Use simulations to approximate the p-value of a correlation coefficient, and use the results to determine whether the correlation between two variables is significant.
Remarks: This benchmark includes having students recognize when arguments based on data confuse correlation with causation. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.S.5.8 (Archived) | Use a regression line equation to make predictions. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.S.5.9 (Archived) | Interpret the coefficient of determination, r², for a least-squares regression. Remarks: Example: A study found the correlation between the weight of a vehicle (in pounds) and its gas mileage (MPG) to be r = - 0.65. What percent of the variation in MPG can be explained by the straight-line relationship with vehicle weight? Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.T.1.1 (Archived) | Convert between degree and radian measures. Remarks: Example: Convert 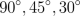 to radians. to radians.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.1.2 (Archived) | Define and determine sine and cosine using the unit circle. Remarks: Example: Find the acute angle,  , for which , for which  Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.1.3 (Archived) | State and use exact values of trigonometric functions for special angles: multiples of 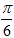 and and 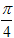 (degree and radian measures). (degree and radian measures).
Remarks: Example: State the exact values of 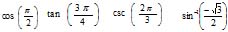 Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.T.1.4 (Archived) | Find approximate values of trigonometric and inverse trigonometric functions using appropriate technology. Remarks: Example: Find the approximate values for 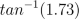 and and 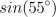 Content Complexity: Level 1: Recall |
| MA.912.T.1.5 (Archived) | Make connections between right triangle ratios, trigonometric functions, and circular functions. Remarks: Example: Angle  is a 50º angle of a right triangle with a hypotenuse of length 14. Find the exact value for sine, cosine, and tangent of angle is a 50º angle of a right triangle with a hypotenuse of length 14. Find the exact value for sine, cosine, and tangent of angle  . .Example: Find the real numbers x, 0 < x < 2p, with exactly the same sine value as  example: find the real numbers x, 0 < x < 2p, with exactly the same sine value as Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.1.6 (Archived) | Define and graph trigonometric functions using domain, range, intercepts, period, amplitude, phase shift, vertical shift, and asymptotes with and without the use of graphing technology. Remarks: Example: Graph y=sin x and y=cos x and compare their graphs. Example: Find the asymptotes of y=tan xand find its domain. Example: Draw the graph of  Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.T.1.7 (Archived) | Define and graph inverse trigonometric relations and functions. Remarks: Example: Graph  Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.1.8 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems involving applications of trigonometric functions using graphing technology when appropriate. Remarks: Example: The number of hours of daylight varies through the year in any location. A graph of the number of hours of daylight throughout the year is in the form of a sine wave. In a certain location the longest day of 14 hours is on Day 175 and the shortest day of 10 hours is on Day 355. Sketch a graph of this function and find its equation. Which other day has the same length as July 4 (Day 186)? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.T.2.1 (Archived) | Define and use the trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant) in terms of angles of right triangles. Remarks: Example: In triangle ABC, tan A = 1/5. Find sin A and cot A. Example: Show that the slope of a line at 135º to the x-axis is the same as the tangent of 135º. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
|
| MA.912.T.2.2 (Archived) | Solve real-world problems involving right triangles using technology when appropriate. Remarks: Example: The elevation of the Pensacola Lighthouse in Pensacola, Florida is 191 feet above sea level. From the top of the light house, the angle of depression to a fishing boat in the Gulf of Mexico is determined to be 15o. How far is the fishing boat from the lighthouse? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
|
| MA.912.T.2.3 (Archived) | Apply the laws of sines and cosines to solve real-world problems using technology. Remarks: Example: You want to fix the location of a mountain by taking measurements from two positions 3 miles apart. From the first position, the angle between the mountain and the second position is 78º. From the second position, the angle between the mountain and the first position is 53º. How far is the mountain from each position? Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.T.2.4 (Archived) | Use the area of triangles given two sides and an angle or three sides to solve real-world problems. Remarks: Example: Calculate the surface area of carpet you need to purchase (in square meters) to cover the floor of a triangle-shaped file cabinet room with sides of length 8 m and 6 m enclosing an angle of 60º. Example: Use Heron's formula to find the area of a triangle with side lengths 4, 7, and 9. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.T.3.1 (Archived) | Verify the basic Pythagorean identities, such as  , and show they are equivalent to the pythagorean theorem. , and show they are equivalent to the pythagorean theorem.
Remarks: Example: Use a right triangle to show that 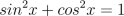 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.3.2 (Archived) | Use basic trigonometric identities to verify other identities and simplify expressions. Remarks: Example: Show that 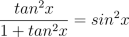 Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.3.3 (Archived) | Use the sum and difference, half-angle and double-angle formulas for sine, cosine, and tangent, when formulas are provided. Remarks: Example: Find and verify the exact value of the 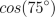 using two different trigonometric identities. using two different trigonometric identities. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.3.4 (Archived) | Solve trigonometric equations and real-world problems involving applications of trigonometric equations using technology when appropriate. Remarks: Example: The diagram above shows a vertical cross-section through some strata, showing that the width (W) of the middle layer, as measured on the upper surface, is not the true width of the layer, T, which is assumed to be constant. Calculate the true width, T, when theta=30º, W=100 meters. Example: Solve 2 sin(x) +1=0 on the interval [0, 2¶)  Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.T.4.1 (Archived) | Define polar coordinates and relate polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates with and without the use of technology. Remarks: Example: Convert the polar coordinates 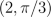 to to  form. form.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.4.2 (Archived) | Represent equations given in rectangular coordinates in terms of polar coordinates. Remarks: Example: Represent the equation 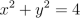 in terms of polar coordinates. in terms of polar coordinates.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.4.3 (Archived) | Graph equations in the polar coordinate plane with and without the use of graphing technology. Remarks: Example: Graph  Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.4.4 (Archived) | Define the trigonometric form of complex numbers, convert complex numbers to trigonometric form, and multiply complex numbers in trigonometric form. Remarks: Example: Write 3 + 3i and 2 - 4i in trigonometric form; multiply the results; and write the answer in a + bi form. Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.4.5 (Archived) | Apply DeMoivre's Theorem to perform operations with complex numbers. Remarks: Example: Simplify  Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| BENCHMARK CODE | BENCHMARK |
| MA.912.T.5.1 (Archived) | Use a variety of problem-solving strategies, such as drawing a diagram, guess-and-check, solving a simpler problem, examining simpler problems, and working backwards, using technology when appropriate.
Remarks: Example: Graph y = sin x + cos x without the use of graphing technology. Students should work problems where they are required to distinguish relevant from irrelevant information, identify missing information, and either find missing data or make appropriate estimates. Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |
| MA.912.T.5.2 (Archived) | Decide whether a solution is reasonable in the context of the original situation. Remarks: Example: Sandy was asked to solve for tan 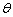 , given that the sin , given that the sin  =3/5 where =3/5 where  . When she completed her work, her answer was tan . When she completed her work, her answer was tan  =3/4. was her answer reasonable for the given problem? justify your decision. =3/4. was her answer reasonable for the given problem? justify your decision.Content Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts |
| MA.912.T.5.3 (Archived) | Determine whether a given trigonometric statement is always, sometimes, or never true. Use the properties of the real numbers, order of operations, and trigonometric identities to justify the steps involved in verifying identities and solving equations. Remarks: Example: Is the statement 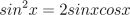 true for all x? true for all x? Explain your answer. Example: Verify that 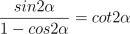 by justifying each step. by justifying each step.Content Complexity: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning |

This report was generated by CPALMS - www.cpalms.org